HERNIA - CAUSES, COMPLICATIONS, AND TREATMENT
By Myupchar, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia
Most of the internal organs of the human body are located in a cavity and surrounded by structures (organs and tissues) that protect them from the external environment. These internal organs are known as the viscera and include the heart and lungs which are located in the chest / thoracic cavity and the intestines, liver, and pancreas which are located in the abdominal cavity.
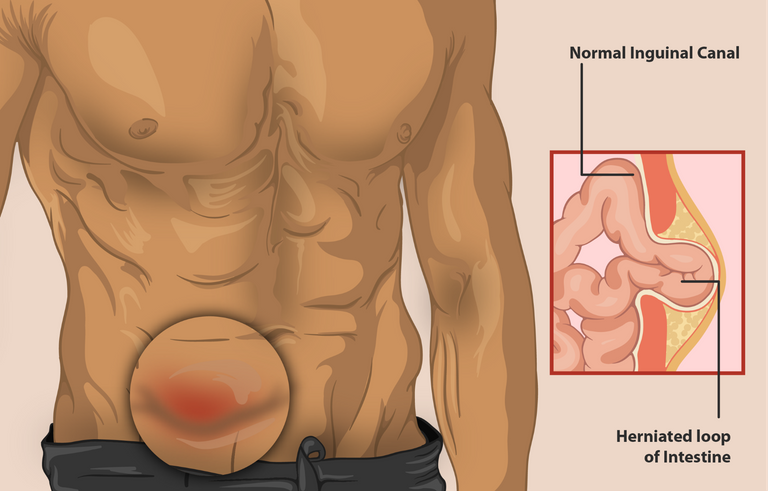
These cavities are formed by intact walls of tissues that protect these internal organs and keep them in place. When there is any defect or weakness in the wall of the containing cavity of any of these viscera (internal organs), the viscus, therefore, protrudes through those defects and that is a condition referred to as a hernia.
Hernias can be internal or external but the common ones that we see are the external hernia and most commonly, the inguinal hernia. For the internal hernia, the protruded organ (viscus) remains inside the body and does not communicate with the exterior. Examples include the diaphragmatic hernia, hiatal hernia, etc.
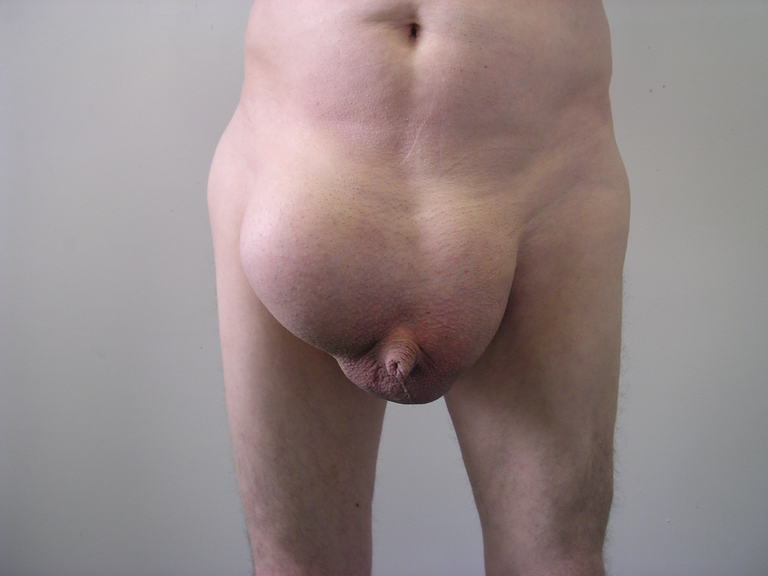
For the external hernia, the protruded viscus communicates with the exterior and we can see the protrusion there or when the person coughs, the protrusion bulges out. Examples include the inguinal hernia, femoral hernia, epigastric hernia, umbilical hernia, etc.
By PacoPeramo - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia
For the inguinal hernia, the protruding viscus is mostly the intestine or fat and the point of weakness through which the protrusion occurs can be either through a point called the Hesselbach triangle (direct inguinal hernia) or the deep ring (indirect hernia). Direct inguinal hernia is commoner in old people while indirect inguinal hernia is commoner in children and young people.
CAUSES OF HERNIA
There are many causes of hernia in our environment, particularly things that cause increased intra abdominal pressure or trauma to the walls of the containing cavities of the viscera. I will highlight some of these cases below;
Lifting heavy loads or heavy exercises.
Lifting heavy loads tend to increase the pressure inside the abdominal cavity. This weakens the walls of the containing cavity of these viscera and over time, a weakness or defect develops through which the viscera protrudes (hernia).A history of chronic constipation or bladder outflow obstruction
This is because the patient strains to pass feces or urine due to constipation or obstruction. This straining increases the intra abdominal pressure and over time, it results in the weakness of the abdominal wall and hernia.A history of Chronic cough and the presence of a mass in the abdomen are other causes of increased abdominal pressure and hernia.
Any form of trauma to the abdomen has also been found to be a cause of hernia. These include previous surgeries like appendicectomy or any form of trauma around the area of the hernia.
Other causes of hernia includes a history of cigarette smoking, multiple pregnancies, peritoneal dialysis, collagen vascular disease, aging, poor nutrition, over weight or obesity, etc.
By Rocco Cusari and Jacopo Werther., CC BY-SA 2.5, Wikimedia
COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA
Usually, uncomplicated hernias only cause mild symptoms or discomfort. In some cases, there may be no symptoms at all. Most persons that come to the hospital just come for cosmetic reasons. However, some complications can arise from a hernia.
One of the most common complications of hernia is intestinal obstruction. As I stated above, the commonest viscera that protrudes through the point of weakness of the cavity in a hernia is the intestine.
Commonly, when it protrudes out, it can be reduced by pushing it back into the cavity or spontaneously when lying down. Most persons who have a hernia, especially an inguinal hernia or inguinoscrotal hernia know how to maneuver and push the protruding viscus back with ease. Here, we say that the hernia is reducible.
However, in some cases, this protruding viscus (intestine) can be trapped in the defect and cannot be pushed back. Here the hernia becomes irreducible. This trapping compromises the normal forward movement of food through the intestine, thereby causing intestinal obstruction.
The symptoms of this intestinal obstruction include vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, and abdominal mass. Intestinal obstruction is an emergency and in my next post, I will discuss intestinal obstruction in detail.
As this trapping continues, the blood supply to the intestine can be compromised too. This is the point of strangulation of the intestine and that part of the bowel can die and form a gangrene. This stage is usually noticed by intense and exacerbated abdominal pain, fever, etc.
There can also be inflammation or rupture of the intestine. When the intestine ruptures, the bowel content is poured inside the peritoneum leading to peritonitis. This is an emergency and needs urgent surgical intervention.
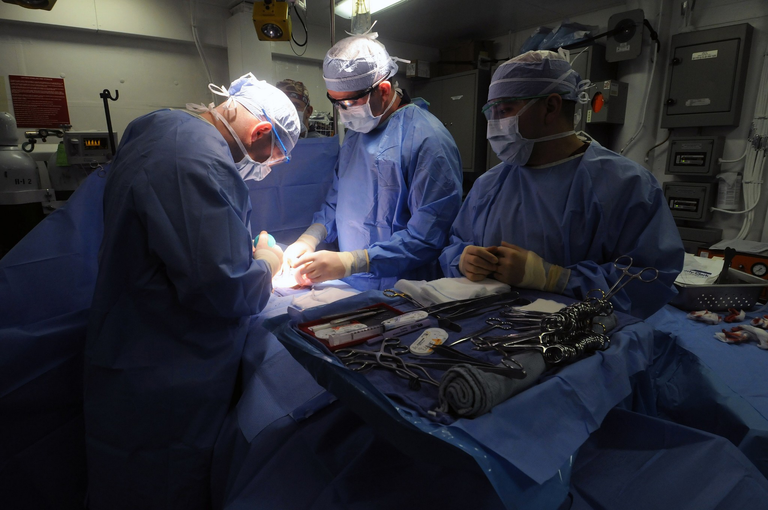
TREATMENT OF HERNIA
The available treatment option for hernia is surgery. The surgery is basically to return the protruding viscus to the containing cavity and repair/reinforce the defect.
The available surgical options are herniotomy, herniorrhaphy, and hernioplasty.
Herniotomy is done in children which involves the reduction of the content and excision of the sac.
By U.S. Navy photo by Mass Communication Specialist Seaman Jessica Echerri - Public Domain, Wikimedia
In herniorrhaphy, the sac is excised and then the posterior wall is reinforced with non-absorbable sutures to make it stronger so that the viscus won't protrude again. While for hernioplasty, an artificial material like the prolene mesh is used to reinforce the posterior wall (area of the defect).
CONCLUSION
Hernias are very common surgical conditions. Normally, there are no major troubling symptoms apart from the protruding mass which is of cosmetic concern.
However, there can be life-threatening complications like intestinal obstruction, strangulation, rupture, and peritonitis. Those who have a hernia and notice any of the signs of vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, fever, etc or the hernia becomes irreducible should report immediately to the hospital for evaluation and treatment.
The treatment of hernia is usually simply surgical with excellent success and recovery rates.
Thanks for reading. You can drop your questions and concerns in the comment box for clarification.
For references and further reading on hernias, please check the materials below;
American Academy of Family Physicians
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Thanks so much for your support @stemsocial .I appreciate