URINARY TRACT INFECTION - NOT ALWAYS AS SIMPLE AS IT'S THOUGHT!
There is the case of this young man who had a urinary tract infection. When he noticed the symptoms, he went to a patent medicine dealer where he got some over-the-counter antibiotics which relieved the symptoms but the infection was not properly treated. Due to the poor treatment, the infection continued and eventually damaged the urethra leading to urethral stricture and urinary retention. The urethra is the pipe that connects the bladder to the exterior. It is the passage through which urine comes out during the voiding/emptying of the bladder.
Due to the urethral stricture, urine could not pass from the bladder to the exterior and therefore the guy could not pass urine again. This caused urine to continue to accumulate in the bladder without any route of exit. This further led to the backflow of urine to the kidneys through the ureters (the ureters are the pipes that connect the kidney to the bladder).
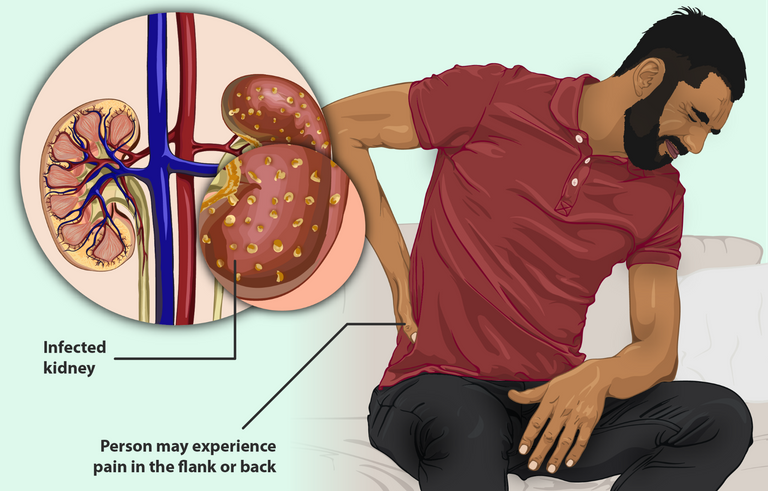
This accumulation of urine in the kidneys is described as hydronephrosis which eventually led to kidney damage in this guy. Before he came to the hospital, he already had a chain of events from urinary retention to ongoing kidney damage. He was managed for kidney failure but sadly he could not make it. Remember that this all started with a urinary tract infection.
So urinary tract infection is not one of those conditions to be treated with self-medication. Untreated or poorly treated urinary tract infections can be disastrous. Before we go into detail on this, let me give a brief overview of what urinary tract infection is and some common symptoms.

WHAT IS A URINARY TRACT INFECTION

Just as the name implies, this is an infection that occurs anywhere along the urinary tract. The urinary tract is made up of 1. The kidneys where the urine is made. 2. The ureters which connect the kidneys to the bladder and serve as a channel through which the urine produced in the kidney gets to the bladder. 3. The bladder where the urine is stored and 4. The urethra which connects the bladder to the exterior.
Any infection in any of these 4 structures as well as the prostrate gland is referred to as a urinary tract infection. The urinary tract can also be divided into the upper urinary tract (kidney and ureters) and the lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra). So you can have an upper urinary tract infection or a lower urinary tract infection depending on the structure affected.
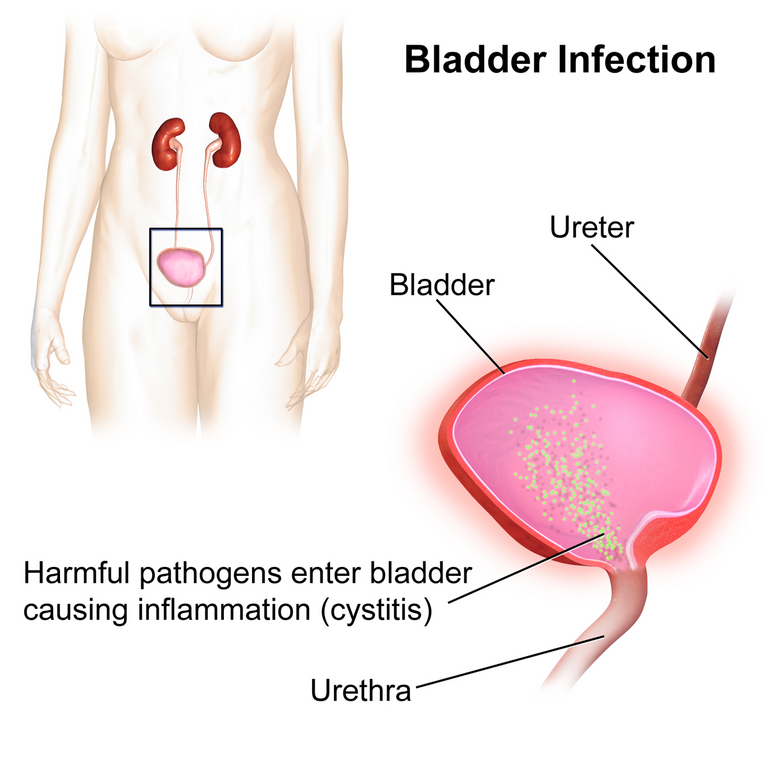
The cause of urinary tract infection is bacteria which in most cases is E. Coli. Other bacteria like S. saprophyticus, k. pneumoniae etc are also common causes. Candida can be a cause of UTI especially in catheterised and immunocompromised patients.
UTIs are commoner in women and most UTIs in women are uncomplicated and respond to antibiotics therapy. UTIs in men are not common but when it occurs, it's most times complicated. In men, it occurs more in infants or the elderly due to urologic abnormalities but it can still occur in young men, especially those who practice unprotected anal sexual intercourse.
Generally, the route of infection for UTI is through the urethra, from where the pathogenic microorganism ascends the urinary tract. It can also spread through the blood and lymphatics but the most commonest is through the urethra.

RISK FACTORS FOR UTI

Many factors predispose individuals to having a urinary tract infection. These are;
Behaviors like voiding dysfunction. Some have a habit of holding on to or delaying the passage of urine even when they are pressed. This habit is not good and predisposes to UTI because allowing urine to stay long in the bladder gives some bacteria enough time to grow and multiply. Those who also clean from back to front after defecation are also at increased risk, especially women. This behavior introduces pathogenic microorganisms from the anal region into the urethra.
Antibiotic use or abuse is another common risk factor. These antibiotics disturb the normal flora of the body thereby giving room for pathogenic microorganisms to grow and cause UTIs.
Other risk factors include indwelling urinary catheters, frequent or recent sexual intercourse, female gender (they have a shorter urethra than men), pregnancy, vesico urethral reflux, familial tendency, etc. Individuals with diabetes and other immunocompromised states are also at an increased risk of getting UTIs.

SYMPTOMS OF UTI

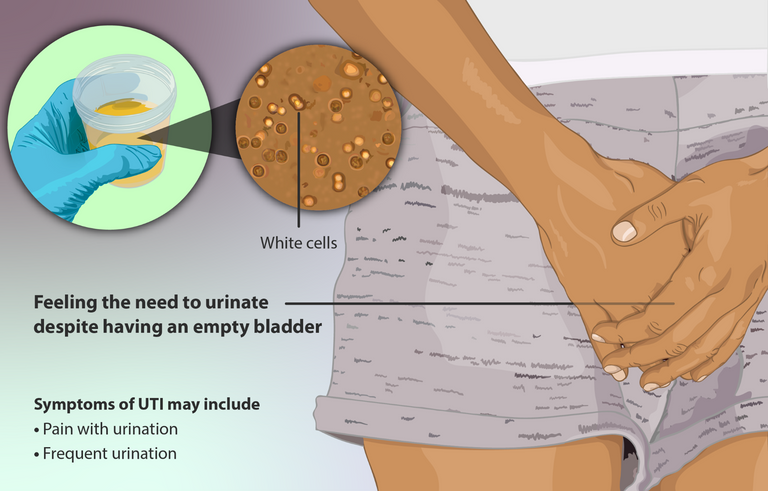
Some symptoms of lower urinary tract infection include painful urination or feeling of a burning sensation while urinating, frequency or urgency of urination, and pain in the lower part of the abdomen (supra pubic pain). For the upper urinary tract infection (pyelonephritis), they present with flank pain, abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and a general feeling of unwell.
With these symptoms, the doctor will recommend some laboratory investigations to aid in making the diagnosis. Tests like Urinalysis, Urine microscopy, culture and sensitivity, full blood count, Serum E/U/Cr, Renal ultrasound scan, etc are usually done as indicated.
The treatment is usually with the required antibiotics either orally for lower urinary tract infection or initial intravenous therapy for pyelonephritis. There may also be an option for surgery in the case of stones and ureteral abnormalities.

WHAT DO WE HAVE TO DO

Urinary tract infection when detected early can be handled with adequate treatment. However, when it is poorly treated or not treated, it might result in unpleasant sequelae or even death.
Therefore, to prevent this adverse outcome, we must see our doctor anytime we notice any of the above symptoms of urinary tract infection. This must be adequately treated with the RIGHT antibiotics, in the RIGHT dose and RIGHT duration.
UTI can be a cause of kidney failure as seen in the case of this man. This kidney failure can also give rise to hypertension and other heart and blood vessel problems. UTI can also cause the presence of microorganisms in the blood (sepsis) which is very fatal.
UTI also occurs in some women during pregnancy and must be treated immediately for the safety of the mother and child.

PREVENTION OF UTI

Some important steps in the prevention of UTI are as follows;
Good perineal hygiene: It is always advised to wash and clean the anal and genital areas at least once a day during showers. This helps to keep away pathogenic organisms from entering the urethra.
Always clean from front to back: Females are encouraged to always clean the perineum from front to back. As I stated earlier, cleaning from back to front will introduce microorganisms from the anal region to the urethra which is a very common risk factor for UTI.
Take enough fluids: Adequate fluid intake helps the kidneys to make enough urine which helps to flush out some bacteria during urination. Adequate fluid intake also prevents the formation of kidney stones and keeps the body well-hydrated and healthier to fight the invading microorganisms.

Regular emptying of the bladder when full to avoid the urine serving as a culture medium for the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
Avoid unhygienic practices: Some commercial feminine hygienic products or douches are unhealthy for the perineal tissues. They can alter the normal bacteria flora and allow the pathogenic ones to grow. They also alter the integrity of the perineal epithelium.
Safe sex practices: Females are encouraged to urinate before and after sexual intercourse, as it can help to flush out any bacteria contamination of the urethra before they invade the epithelium. Unprotected anal intercourse is also discouraged for men as the bowel flora from the anal region can easily get into the urethra and cause UTI.
In conclusion, UTI is one of the commonest bacteria infection in man. It is simple and easy to treat but can be disastrous too. Therefore, we must avoid the risk factors and also go for proper treatment when we notice the symptoms. Some may not even have symptoms at the early stage and that is why medical check-up is also important from time to time as well as total adherence to those preventive measures stated above.
Thanks so much for reading.
For references and further readings, please check the resources below;
I love ❤ this information, when it comes to health and well-being of humans am always interested. Just like you said
Thank you for sharing.
Yeah, indeed health is wealth and we must always protect ourselves from the various diseases around us.
Thanks for your wonderful contribution ma.
Thank you for sharing
Very informative. The suggestions you have given are really important.
Thanks for sharing ❤
You're very welcome Sir. I am glad that you found it helpful.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Many thanks. I appreciate your support @stemsocial
Antibiotics can cause UTI, and then you need antibiotics to treat it. Seems like a double-edged sword!
Yes, every drug or biomolecule is always a 2 edged sword, depending on how it is used.
When antibiotics are used indiscriminately, it predisposes to UTI but when the right antibiotics is used in the right dose and right duration, it treats UTI.
This is because the body maintains a critical balance of normal bacteria flora which are beneficial to man. But when this balance is altered by injudicious antibiotics use, it predisposes the body to invasion by the problematic (pathogenic) organisms which now cause infections for man.