DAGs: What are they and how do they work
Blockchain technology was an innovation that made room for databases to acquire much more complex and representative dimensions. It made it possible for a universe of applications to be developed and become sufficient to lead to the emergence of a series of extremely disruptive solutions.
Two major structural problems still need to be overcome so that its full potential can be reached: usability and scalability. And DAGs can play a very important role in solving both problems.
What are DAGs
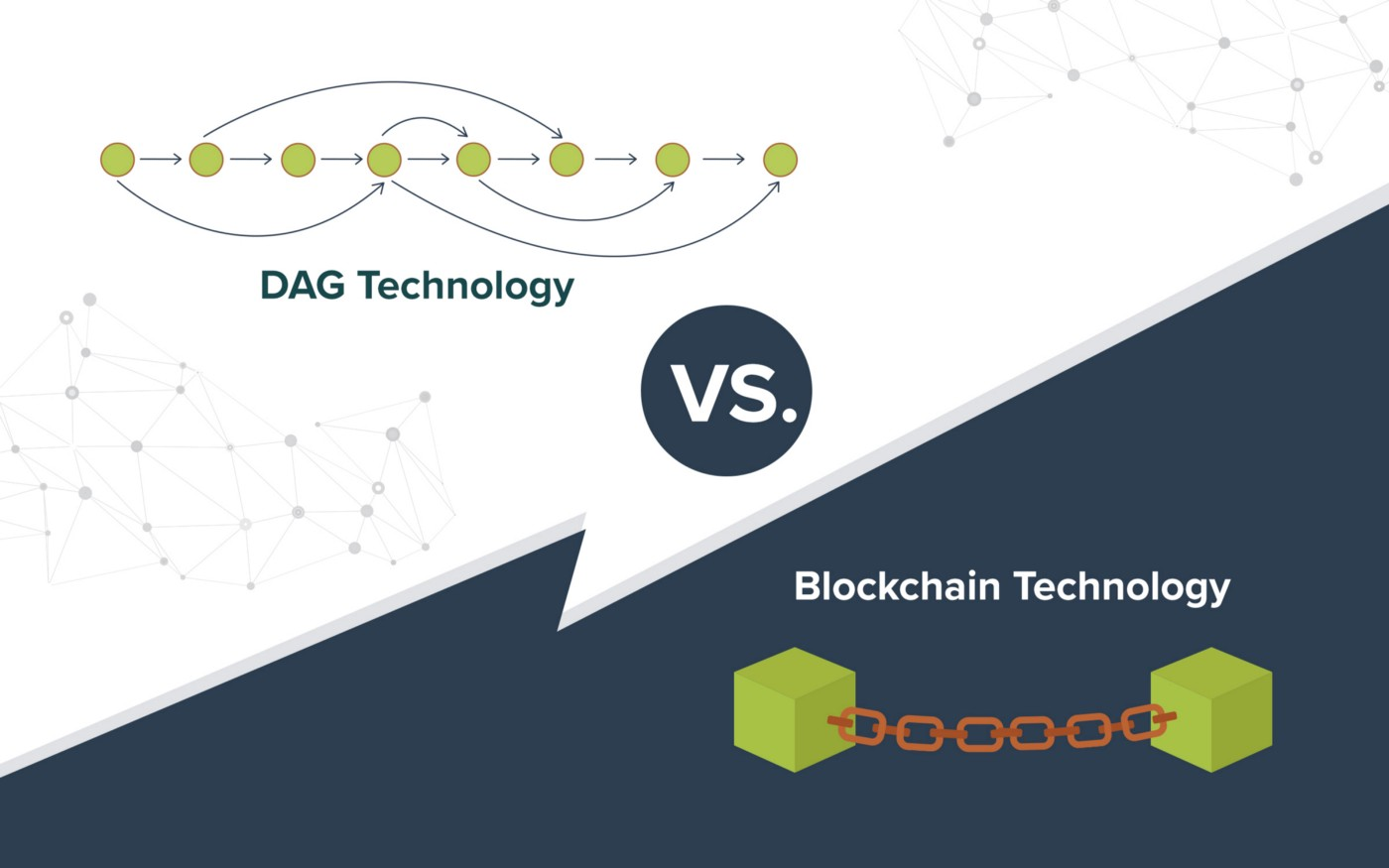
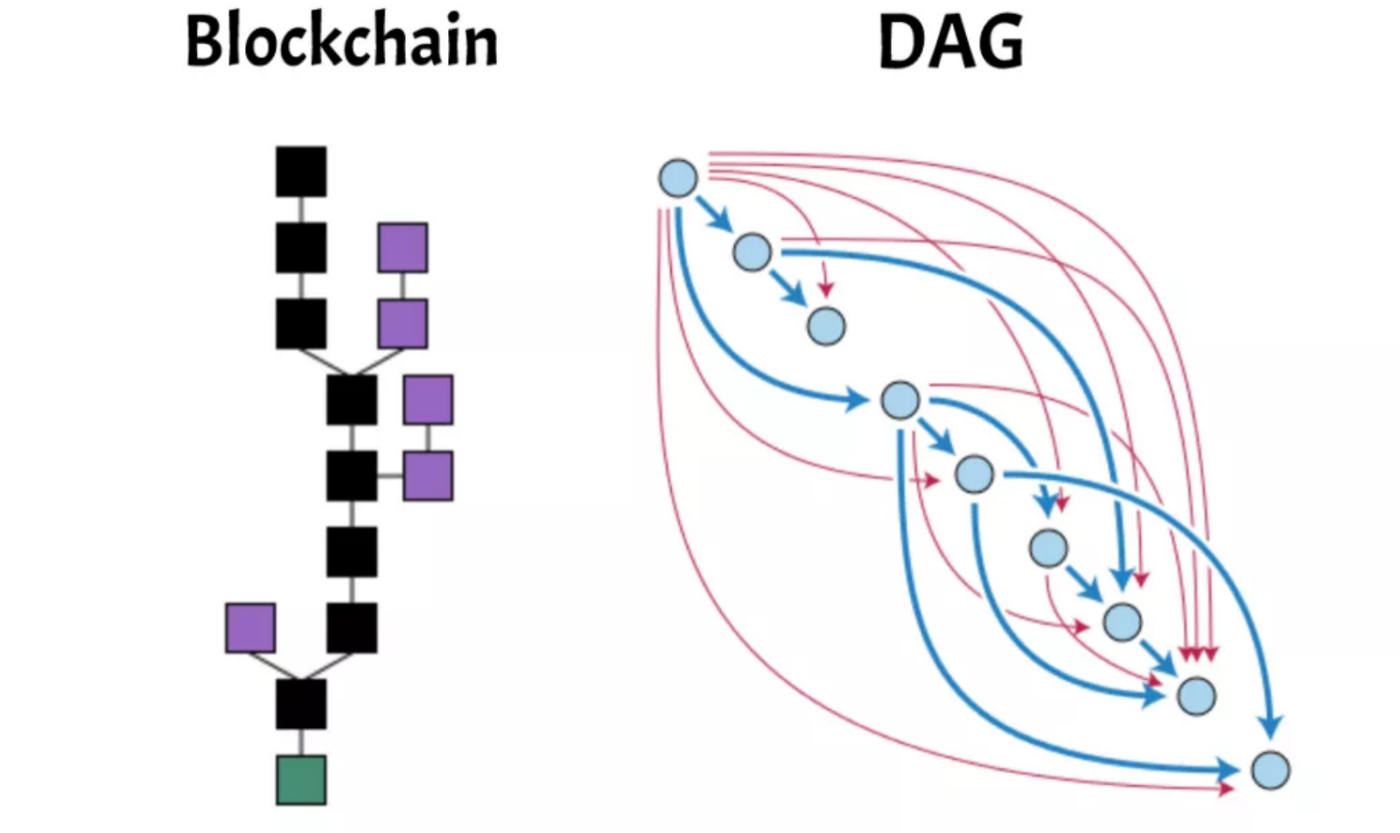
The acronym DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph. It is a data organization architecture that has a different model from that used by blockchains. In it, information is not transmitted in blocks, but through circles and lines.
The circles contain a set of transactions that need to be registered on the network, and the lines represent the order in which they will be executed. The data flow only finds its way between the circles moving forward, so the architecture is acyclic. And all the lines point in the same direction, so it is also directed.
As with blockchains, new transactions cannot stand alone and need to be built on top of existing transactions. However, its great differential lies in the fact that its model allows the simultaneous validation of numerous transactions. That is, a much larger volume of data can be processed in a circle, dramatically increasing scalability.
Furthermore, in the system used by DAGs, users are also the validators of transactions. Before they have their own transactions validated, they need to validate two others. Only after that will your transaction be considered for validation by other users. Thanks to this feature, mining is not required, transaction fees and environmental impact are minimal.
Structure and functioning
DAGs are a type of DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology), just like Bitcoin and other blockchains. This means that in its structure there are nodes, which need to be validated so that there is consensus and transactions are registered on the network. Each node has a depth dimension, which allows the allocation of an almost infinite number of transactions.
For a node to validate a transaction, it must solve a cryptographic puzzle similar to those on the Bitcoin (Proof of Work) network. An algorithm selects two blocks, which need to be validated by users/validators so that their transactions follow the flow within the network and are confirmed.
Security and reliability
Although it contains a known, tested and validated mechanism, the scalability potential of these networks has not yet been stressed to the fullest. It is not known whether, when pressured by a very large volume of transactions, a DAG would always behave in the same way and remain stable. As their adoption expands, unexpected complications may arise.
And DAGs with low trading volumes also have a downside. They are more susceptible to being attacked. Its architecture depends on a large volume of transactions being carried out so that the system is more secure and efficient.
DAGs that are reference
Although DAG technology is relatively recent, there are already a good number of networks that use it. Most of them rely on scalability differentials and very low transaction costs to develop solutions for problems that involve a very large number of transactions.
IOTA

One more acronym for you to keep: Internet of Things Applications. IOTA is a network focused on the Internet of Things. In case you don't remember, Internet of Things is the set of technologies that makes it possible for objects of different types to be connected and can be controlled through the internet.
In operation since 2016, IOTA is a pioneer DAG. It is very likely that in the near future more and more IoT (Internet of Things) use cases will appear and the efficiency of DAGs will be tested from this protocol. It's worth keeping an eye on his development!
NANO

Nano is focused on offering DeFi solutions. It develops applications that enable the transfer of values between users in a decentralized and secure manner. It is also possible to buy products using the currency (native token) of the network. On the website there is a section where you can receive a faucet to test the network's functionality.
Uncomplicated financial transactions, without cost and with agility. This is what Nano intends to offer its users using DAG technology. This is a very representative segment with regard to the use of disruptive and innovative technologies.
IoT Chain (ITC)

Also focused on Internet of Things solutions, IoT Chain is one of the most representative DAGs today. It has been receiving investments from several important Chinese companies, even surpassing several blockchains. Its network can process more than ten thousand transactions per second.
If we imagine a near future in which almost every household object we use is connected to the internet, from light bulbs to faucets, we can envision a scenario in which DAGs will have their opportunity to prove themselves as a challenging alternative to blockchains.
Considerations
DAGs are a very interesting, relatively new technology with incredible potential to solve problems that seemed extremely complicated for blockchains. But that doesn't mean that one should replace the other. In fact they can compete in some circumstances, but it is very likely that they coexist, developing individually.
Networks like Ethereum are already finding solutions to increase their usability and reduce their impact on the planet. Other technologies should emerge to make blockchains even more efficient and help them increase their scalability. Both aspects have been questioned since the emergence of Bitcoin, but it was never enough for users to stop using it.
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
https://twitter.com/CryptoSimplify/status/1575066329849024512
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people( @cryptosimplify ) sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.
1st time hear about DAGs, but it seems very interesting topic
Nice to have shared new things with other community members
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
Yay! 🤗
Your content has been boosted with Ecency Points, by @cryptosimplify.
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for new Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more
Sorry i missed !1UP command, take care!
No problem at all and thanks for the support
You have received a 1UP from @kwskicky!
@leo-curator, @vyb-curator, @neoxag-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
Fantom is the best DAG in my opinion because it is EVM compatible, has super cheap and fast transactions and the team is rolling out a new Fantom Virtual Machine in 2023.