Hematology || Polycythemia - The Increase in Erythrocyte
Over the past few days, I have been taking us through hematology. Started from Erythropoiesis, where I explained the Red blood Cell formation, to explaining the life cycle of the Red Blood Cell. In those posts, we saw that the red blood cell is being produced in the Red Bone Marrow, by the myeloid stem cells which becomes an Erythroblast, which develops to become a reticulocyte, after which it gets matured to become a red blood cell, and it is pushed into the bloodstream where it distributes oxygen to the body, and take CO2 to the lungs. After about a period of 100 to 120 days, the red blood cell becomes old, and rigid, where it is destroyed by the spleen. You can read through my previous post from my blog, and I will be putting the links to the posts after the completion of this post. Today, I will be sharing with you a topic still on Hematology, and that's polycythemia.
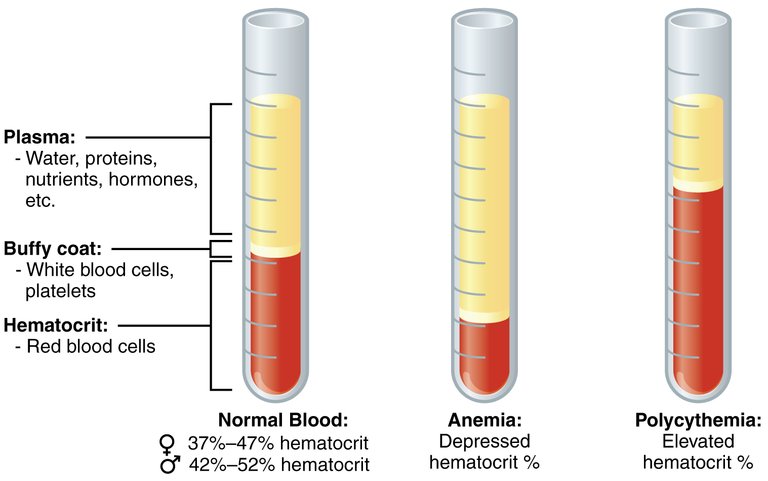
Polycythemia will be characterized as an abnormal increase in hemoglobin, an increase in hematocrit level, and an increase in the red blood cell. The Hematocrit range for men is 45% - 52% for men, and 37% to 48% in women.. Polycythemia can be categorized as relative or absolute (which can be divided into primary (Polycythemia Vera) or secondary polycythemia).
Relative Polycythemia is regarded as the increase in the hematocrit level due to a decrease in the blood plasma. This could be as a result of lowered fluid intake (water), diarrhea, and increased sweating.
With these two types of absolute polycythemia, there is an increase in either the red blood cell, the hemoglobin and the hematocrit. In Polycythemia Vera/Primary Polycythemia, there is a problem with red blood cell production. The problem usually occur in the bone marrow, when there is a dysfunction/mutation in the JAK-STAT pathway causing the JAK2 to be active without the presence of Erythropoietin (EPO), leading to the excessive production of Growth factor for Red Blood Cell, causing the production of more red blood cells than usual.. With more red blood cells in the bloodstream, the viscosity of the blood increases, causing the blood to be thicker, which could lead to an increase chance of thrombosis or embolism. The common type of Polycythemia vera JAK-STAT mutation is the JAK2 V617F, TET2, and JAK2 EXON12. Where there is an increase in the production of red blood cell, thereby causing excessive amount of RBC in the bloodstream, so will there be an increase in the death of the RBC, causing the increase production of Uric Acid and Gout.. With Polycythemia Vera, platelets could start to clot, causing Erythromelalgia in the extremities of the body. When the blood is viscous, it could lead to splenomegaly, where the Spleen becomes enlarged as a result of increased work to do.
In Primary polycythemia, is another disease called Primary familial and congenital polycythemia (PFCP), which causes uncontrolled production of Red Blood Cells. It is caused by the mutation/hypersensitivity of erythropoietin (EPO) receptor, instead of the JAK-STAT pathway, thereby causing the production of excessive red blood cells. PFCP can cause Vertigo, Venous thrombosis, Pruritus, Epistaxis and other Hyperviscosity syndromes like headache, diziness and so on..
Secondary Polycythemia is an increase in the Red Blood Cell mass, as a result of increase in the erythropoietin (EPO) hormone due to tissue hypoxia, or low oxygen levels in the tissues. EPO production could be triggered by, High altitudes where oxygen is reduced, Respiratory disorders, Heart diseases, Sleep Apnea, Kidney problems, genetic defects, and certain tumors such as hepatocellular carcinoma, uterine fibroid tumor, renal cell carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, and hemangioblastoma of the brain., . Secondary polycythemia usually have an underlying factor which allows for the increase in the mass of the red blood cells.
Mutations in genes could also lead to an increased erythropoietin EPO production. A mutation in the PHD-VHL-HIF axis, the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Pathway that is critical in the adaptation of tissues to low oxygen environments via transcriptional regulation of genes, could lead to an increase in Erythropoietin (EPO). . All nucleated cell have the HIF-1α which acts as a transcription factor allowing the regulation of genes for EPO. Von Hippel Lindau (VHL), which is attached to HIF-1α, through the help of the enzyme Propyl hydroxylase domain 2 (PHD2), which is responsible for oxygen-induced degradation of HIF-1α, and it allows VHL to act as a marker for HIF-1α which will lead to the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of the protein. When this doesn't happen due to mutation in either the PHD2, or the VHL, the HIF-1α isn't targeted for destruction, thereby causing it to remain and start to trigger the production of the hormone erythropoietin (EPO) which would lead to increase in RBC in the blood despite normal oxygen levels..
Treatment for secondary polycythemia can vary depending on the underlying cause of the polycythemia. In most cases, focusing on relieving the hypoxia is key. Phlebotomy could be used to reduce the RBD in the body. In cases where it requires surgical removal of the tumor producing erythropoietin (EPO), Surgery should be done to remove lesions., .
Conclusion
A lot of athlete illegally use polycythemia (the increase of hemoglobin (RBC)) to cheat in spotting activities that requires the use of Oxygen via Blood Doping. With Blood doping, Athletes will be able to boost the oxygen that will be distributed to the muscles, thereby allowing them to last longer (endurance) on the field or track without getting exhausted. They can do this by blood transfusion, and injecting erythropoietin. Blood doping without proper hydration could lead to stroke, cerebral embolism, and thrombosis.
Image
Image 1 || Wikimedia Commons
Link to My Previous Posts
Excellent your post, I like so much, congratulation, greetings from Cuba 🙋🙋🙋
Thanks a lot for this, 😘😘
I love this content, nice and interesting.
My greatest concern with polycythemia is the risk of thromboembolism. With the increased viscosity of the blood, it can easily clot and embolise to distant organs causing great damage or even death.
I also learnt a new thing here about the concept of blood doping by athletes using the principle of polycythemia.
Thanks alot for sharing.
Thanks a lot for reading my post. Blood doping is illegal now in sport, but it is surprising what people can do for more oxygen and energy for muscles in sport
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Hmmmm.... I noticed I have missed some very interesting posts from you. The lifecycle of our red blood cells is definitely something about which I would like to know more (and I enjoyed the parenthesis on the athletes, in your conclusions).
I have therefore added the previous blogs you wrote to my to-read list for the next few days. Thanks!
Cheers!
This is really heartfelt, I must confess @lemouth, I am really glad that you are setting out time to read my content. Thanks a lot.
You are very welcome!