Refraction of light explained - with examples

Introduction
Light travels in a straight line. You do not need to do an expensive experiment to confirm that. Just flash your car headlamp at night and you will observe that the light moves straight ahead of you. Or when you flash a torch inside an enclosed building, you will observe that the torchlight travels straight. So when light moves through any one medium, it maintains a motion of straight line. However, there are situations when light appears not to travel in a straight line. This nature or property of light to change direction explains some of the physical phenomena we observe around us.
In this discussion, we will learn how light behaves when it moves from one medium to another. A proper understanding of this would help explain a lot of situations that look real, but are just an illustration of the motion of light across different media.
The following situations are as a result of refraction of light:
- When you look at the bottom of a swimming pool, it appears shallower that it actually is
- When partially placed in a liquid, a spoon appears bent
Now before we go into the above two examples, let us explain refraction of light properly.

How light behaves when travelling across two mediums
Light does travel in a straight line when it moves across the same medium like in air. It however changes its direction as it enters a different medium. This often happens because each medium like air, water and glass have different densities. The speed of light in each thus differs because of the difference in their densities. Hence as it moves from one medium, it immediately changes its direction at the boundary of the next medium it enters.
The ability of light to change its direction when moving across different mediums is known as refraction of light. Thus, the direction of light tends to significantly change as it enters one medium from another. The illustration below is used to explain this phenomenon:
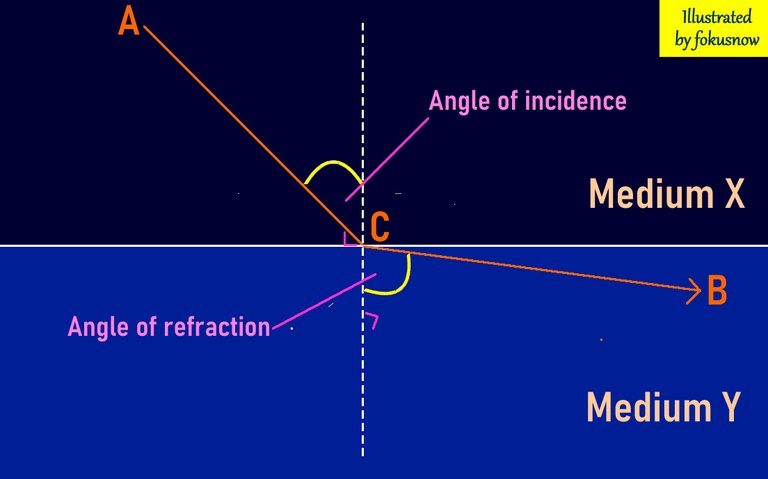
The above diagram explains how light moves from one medium to another and changes direction in the process. It started travelling from point A in Medium X (which could be air for example) and moved pint B in another medium Y (glass or water). ACB represents how the light travelled.
Now notice that at point C where the light exited Medium X and entered Medium Y, the direction or path of the light changed significantly. This happens because the light has entered a medium whose density is different from the medium where its journey originated. It makes two noticeable angles that will be explained below:
Angle of incidence: This angle is made by the ray of light with the exit point of its journey in the first medium. The intersection of that ray of light with the surface of the medium it is about to leave. It is at this point that the direction of light significantly deviates from its original path. This angle is made at points C from A.
Angle of refraction: As the light moved into a different medium with different density, its direction changed very noticeably. The intersection of the ray of light with the surface of the new medium creates an angle. From this point where the deviation is noticed, the ray of light has refracted. Thus, this angle is known as angle of refraction.
Important observation
Considering the two angles of incidence and refraction, it is observed that the later is much bigger than the former. The angle of incidence is often noticed to be a little smaller than the angle of refraction. This often happens when it travels from a more dense medium to a less dense medium. As the light enters a medium that is less denser, the refracted ray of light bends away from the original path, hence creating a bigger angle with the new medium. It is also the other way round. The refracted ray bends towards the normal ray when light travels into a more dense medium from a less dense one.

Refraction of light in nature
There are many natural phenomena where refraction of light is often noticed. Two of them were mentioned at the beginning of this article.
- A shallower swimming pool bottom: When a person stands and looks straight into a swimming pool, the bottom appears closer, making the pool look less deeper than it actually is. That is a function of refraction of light.
As the light moves from water into the air, its actually travelling from one medium to a different one before it gets into the eye of the person looking. Thus, the light bends and shifts the natural position of the pool bottom. It thus appears shallower. The actual depth is known when the person jumps into the pool
- Spoon appears bent when partially submerged in water: Just pour some water into a bowl and put a spoon to lean on the bowl into the water. It will be observed that at the point where the spoon's handle enter the water, it appears bent. This is refraction of light as it moves from air to water, it tends.

Conclusion
Refraction of light occurs naturally. Light bends as it moves across different media with differing densities. Other examples of light refraction includes reading with a glass and light travelling through a glass prism.
Reference
Note: All Images are mine.
Posted Using InLeo Alpha
It took me a hard time understanding refraction of light in highschool. All my teacher did was theory. I started getting the sense of it with the help of the 'spoon in water' experiment which I did myself. Looking directly, nothing happens but when you view probably from the side. It all made sense and you did great with the illustrations!
Yes some of those topics our science teachers didnt do enough to bring them home. Its only now that we are trying to make them make sense. Refraction of light was one topic I got back then. I remembered how we peered through the glass prisms and plotted the new position of refracted light on the other side.
Far easier now to grasp.
Yeah we did that too, but it was just to pass WAEC 😄
You know na. Thats an unfortunate thing about our school system. Just to pass exam
It's never getting better
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.