Orf Virus, A Viral Infection Affecting Sheep, Goats and Humans.
For some time now, I have consistently written about different infections and viruses that affect our lovely pets, and because dogs and cats are the most popular pets (at least, where I come from), but there are so many other pets around the world that are not so popular, but they are someone's favorite pet. That is the reason why today we will be studying together about Orf virus which causes infection in goats and sheep.
Source
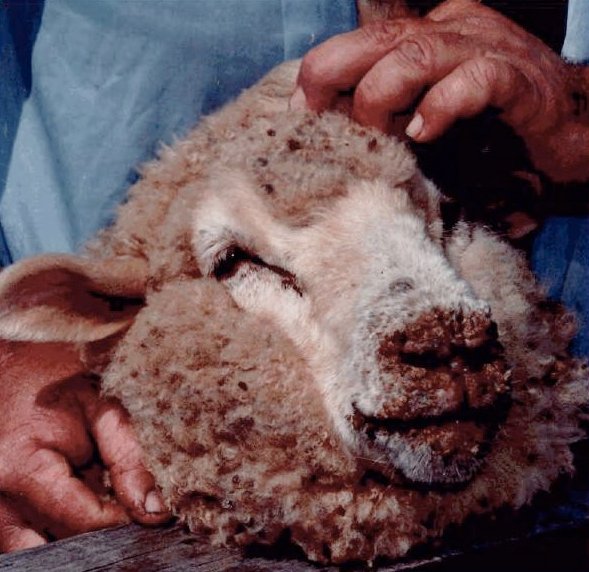
Orf virus is a member of the parapoxvirus genus in the Poxvirus family, although this virus is zoonotic as it can be transmitted to humans, orf infections in animals are usually referred to as; scabby mouth, sore mouth, or contagious ecthyma. Animals that are infected with orf virus typically develop lesions (scabby sores) around their muzzle, lips as well as the mouth. Humans can get the virus if they have a sore, a scratch, or a cut that touches an infected animal, having constant contact with goats or sheep puts humans at such risk.
Early infection stage of the orf virus in sheep and goats, sores appear as blisters developing into crusty scabs. Sheep and goats may get sores on their lower leg and their teats, especially when ewes are nursing infected lambs or kids. There are some other diseases that look like the orf virus, that is; food and mouth disease (FMD), which is a serious contagious and often highly fatal viral disease that can affect goats, cattle, swine, and other cloven-hoofed animals.FMD is usually confused with similar but less harmful diseases including orf infection. On the other hand, do not also confuse FMD for orf virus, if your animal begins to show more severe symptoms beyond having lesions in the oral cavity, teats, and excessive salivation or lameness, it should instantly be reported to a vet.
The virus can be spread from one animal to the other, and materials from the lesions of an animal that is infected can be transmitted to another animal without the virus through cuts or abrasions in the skin. This virus can remain in an environment for months and even last for years, bedding, feed, feed materials, and buildings can get contaminated with orf virus from released scab or lesion material making it highly difficult to totally get rid of the orf virus from the immediate environment as long as the infected animal remains present.
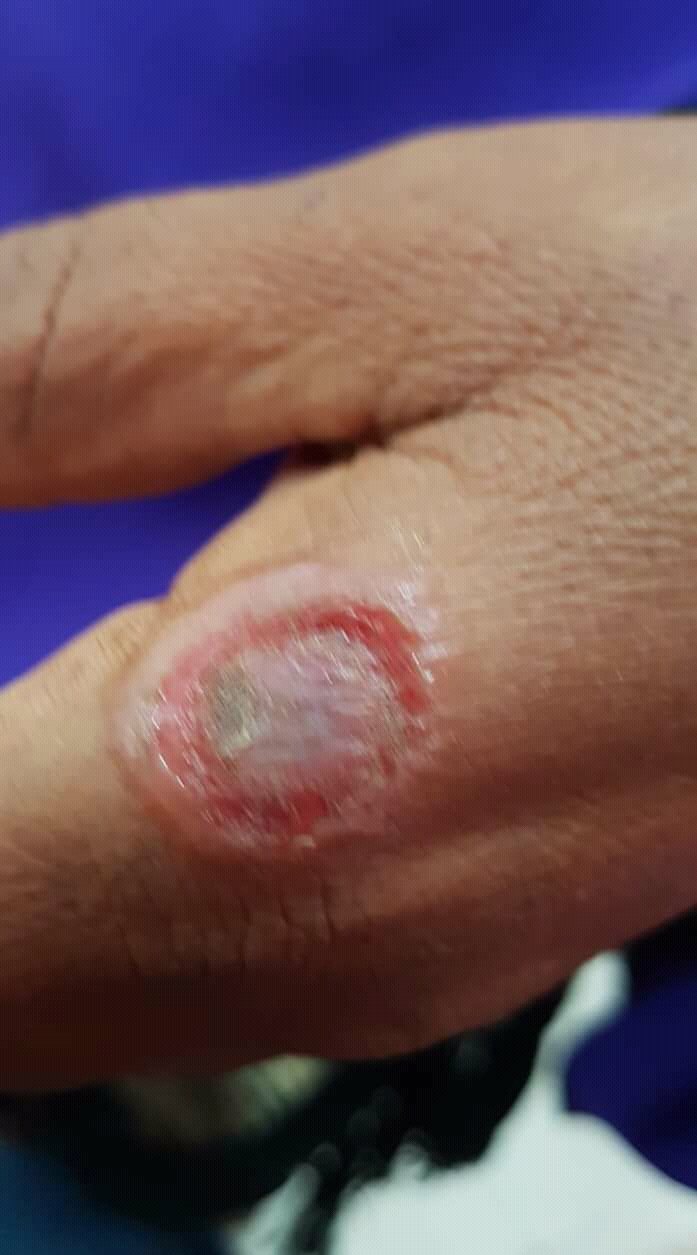
I already mentioned earlier that, the orf virus can be transmitted to humans through blisters and sores but the question is, how do we know that it is of virus we are dealing with, since I am passionate about both pets and pet owners, I will be discussing the sides of humans as well. The blister in humans is usually 2-3cm but it can grow up to 5cm, which may leak fluid before it crusts over. Humans also experience fatigue, high temperature, and swollen glands on the inside of their elbow or under the arm alongside the blister.
Source
Rush immediately to a medical expert if you have any of these symptoms;
If you have a mark or blister on your hand, finger, arm, or face that has gotten bigger or has not healed after 6 weeks.
If you have a painful blister or mark, or if the blister is red, swollen, and painful, and of course, if you have a high temperature.
If you have a rash that appears like a bulls-eye target with a dark center, surrounding a paler ring and a darker ring appearing on the outside.
If you have several blisters, big or painful blisters, or that blister that continues to re-occur.
There is no certain treatment for treating orf in humans, the skin blisters should clear up on their own within 6 weeks, and ensure it is appropriately covered to keep it clean and prevent them from getting infected. With an infection, there will be the requirement for antibiotics. Isn't it better to prevent yourself from getting orf virus than looking for treatment? In order to protect yourself or family members from getting orf virus, make it an habit to wear latex gloves whenever you are touching a goat or a sheep, also wash your hands with warm water and soap especially after touching an animal, clean and disinfect barns and sheds where livestock are kept, vaccinate your sheep and goats against orf virus.
Was I not just speaking about why it is important to stay away from orf virus, that was highly important because it could bring about some form of complications if not treated appropriately and timely. Orf has more impact on some people than others, you stand a higher risk of getting orf virus if you have a weak immune system like an HIV condition or a chemotherapy treatment. Associated complications are; bacterial infections, a rash that appears like a target or bull-eye (erythema multiforme), and a skin condition that causes large blisters (bullous pemphigoid).
Conclusion.
Orf virus is a zoonotic disease that basically affects sheep and goats, then can spread to humans as well. I have mentioned preventive measures in this post and it is always safe to practice safety while handling animals, of course, we should also watch out for symptom changes in our animals and take them to see a vet as long as there is a noticed change.
Hello, I congratulate you on the article, I would like to leave a small opinion, from what little I know of the virus in humans it can leave skin lesions reaching the point of becoming ulceration, the recommended treatment is either with creams or topical antibiotics.
Thank you so much for your time @jrevilla for the contribution, I really appreciate it.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.