The muscular system

from PxHere
Many people, when they think of muscle, picture ripped attractive men and women who have trained to increase their muscular mass. However, muscles contribute significantly more to society than just their aesthetic worth. They ensure the body can move freely, stands upright, and stays in that position. Did you know there are more than 650 distinct muscles in your body? Even though it may not look like it, a caterpillar has close to 4,000 muscles. Caterpillars have incredible muscle control, allowing them to do things like bend and extend to reach leaves on higher branches. It's just one of the fascinating facts about animals that can be discovered.
Having no musculature would render us immobile. The musculoskeletal system's main function is movement. Did you know that when your muscles tense, you generate 85% of your body's heat? Muscles also protect our organs from the outside world. Muscles are essential for the tasks we perform every day because they enable us to move around and maintain our equilibrium. Regular exercise also helps improve health by fostering the growth of strong, healthy muscles. To put it simply, your "guts" and other internal systems rely on the strength of your abdominal muscles. In order to make a pout or deliver a passionate kiss, you need to contract the circular muscle that surrounds your mouth. Sphincters, which are made up of other cylindrical muscles, control urination and defecation. You use a major muscle in your body, the diaphragm, every time you take a breath. If your diaphragm suddenly failed, you would cease breathing and die within minutes. When you breathe, roughly 75% of the oxygen you take in is moved by a muscle called the diaphragm, which is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen. While inhaling, it flattens and compresses to make room for air to enter the lungs, and while exhaling, it relaxes and pushes air out.
Skeletal muscles, which make up the vast bulk of your muscular system, include the ones that wrap around your abdomen and compress your digestive organs and the food you eat. Aside from skeletal and striated muscle, the only other types of necessary muscle cells are cardiac and smooth muscle. Comparatively speaking, cardiac muscle is only located in the heart, while the smooth muscle is widespread throughout the body's blood vessels and organs. The cardiac muscle in your heart contracts in a pattern that causes your heart to beat. There is a great deal of smooth muscle in your reproductive system, cardiovascular system (your blood vessels), respiratory system (your bronchioles), digestive system (your oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines), and urinary system (your ureters and urinary bladder). (uterus, vas deferens).
As was just stated, skeletal muscle is responsible for a lot of the homeostatic regulation that occurs in our bodies. However, not all muscles are under conscious control. For example, smooth muscle in the uterus and vas deferens contract involuntarily during childbirth and ejaculation, respectively. Contracting our skeleton muscles causes our bodies to generate heat. Your muscles contract more forcefully when you're chilly so that they can generate more heat and keep you warm. This is what we know as shivering. Skeletal muscle activity increases during exercise, leading to an increase in heat production and, ultimately, a rise in internal body temperature. The sweat you generate is your body's way of cooling down from the heat. The diaphragm is a skeletal muscle that allows us to take in air when it expands and push out carbon dioxide when it relaxes. This muscle's function is crucial and can't be jeopardized in any manner. The diaphragm is a vital part of our breathing mechanism.
What Makes Up the Muscular System and How It Works
Skeletal muscle is a type of muscle that attaches to the skeleton via tendons. Dense and symmetrical fibrous tissue called tendons attaches muscles to bones. To add to that, the abdominal muscles are held together by dense tendon sheaths called aponeuroses. Seymour's injury was likely caused by a muscle tear or avulsion from the aponeurosis, which normally holds the muscle fibers together. Muscular tissue can be divided into three distinct kinds. Characteristics of skeletal muscle include the capacity to contract on its own, a close connection to the skeleton, and a striated (or striped) appearance. ventricular chambers house the striated and unregulated ventricular muscle. Visceral muscle, or smooth muscle, is a form of involuntary muscle that lacks striae. Tissues and blood vessels all around the body contain smooth muscle.
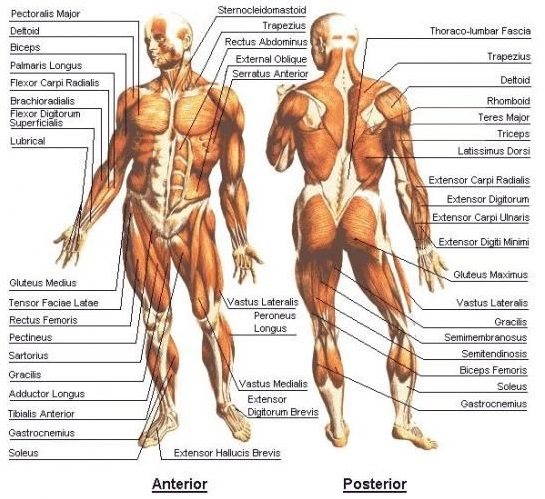
Picture from wikipedia
Every strand of muscle is made up of muscle cells. These fibers are bundled together and held in place by connective tissue. One of the most important parts of a muscle cell is its sarcomere. Muscle contraction is caused by the sarcomeres shrinking. The proper functioning of every type of muscle tissue depends on the mineral calcium. In this unit, you'll learn about the role calcium plays in muscular contraction. Myosin and actin are the two most abundant proteins in skeletal muscle. A nerve impulse is required for skeletal muscle to contract; otherwise, the muscle will not tighten. In order for the muscle to tighten, this instruction must first reach the muscle. Communication between the skeletal muscles and the nervous system is facilitated by chemical mediators called neurotransmitters.
The chemical acetylcholine is responsible for the contraction of skeletal muscle after being stimulated by nerve impulses. The training material will center on the cellular processes that lead up to and result in muscle contracting. One cannot generalize about muscle cells and fibers. Cells known as slow-twitch fibers have specialized in the evolution of long-distance rivalry. Some muscular tissue also contains cells or fibers that are more suited to power and sprinting. Fast-twitch strands are much quicker to tire.
Knowing how muscles contract requires a thorough grounding in the microscopic anatomy and biochemistry of the musculoskeletal system. You will also gain an understanding of the gross anatomy of muscles, including their titles, locations, and functions. The skeleton system contains many fascinating structures. It'll be exciting to figure out your destination as you go.
References
- CCCOnline. n.d. Muscular System Introduction – Anatomy & Physiology. Muscular System Introduction – Anatomy & Physiology. https://pressbooks.ccconline.org/bio106/chapter/muscular-system-introduction/.
- Introduction to the Muscular System | SEER Training. n.d. Introduction to the Muscular System | SEER Training. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/muscular/#:~:text=The%20muscular%20system%20is%20composed,the%20result%20of%20muscle%20contraction.
- Muscular system - Wikipedia. 2016, October 1. Muscular system - Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscular_system.
- Muscular System - Muscles of the Human Body. n.d. Innerbody. https://www.innerbody.com/image/musfov.html.
- Human muscle system | Functions, Diagram, & Facts. n.d. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/human-muscle-system.
- Buckley, G. 2017, February 10. Muscular System - Definition, Function and Parts | Biology Dictionary. Biology Dictionary. https://biologydictionary.net/muscular-system/.


Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.