Chromatography: Unraveling the Science of Separation |ChemFam #64|
Greetings to everyone! Chromatography, often called the science of separation, is a fascinating and indispensable technique that weaves its way into the tapestry of our everyday lives. It's not just a complex scientific method; it's a powerful tool that influences various aspects of our existence. From ensuring the safety of what we eat and the medicines we take to helping solve crimes and fueling scientific discovery, chromatography is a hidden hero that touches our lives in countless ways. So gear up for an another chemophilic ride, fastened up your seatbelts and let's delve into a closer look at the profound significance of chromatography and its diverse applications.

What is Chromatography?
At its core, chromatography is all about separating things. It's like sorting out a jumbled box of crayons by color, only on a much more sophisticated level. The magic happens through the dance of two phases: a stationary one (usually a solid or liquid) and a mobile one (a liquid or gas). As a mixture is coaxed through the stationary phase, its individual components move at different speeds, leading to their separation based on characteristics like size, chemical properties, and even how they interact with each other.
Chromatography is a technique used to affect the separation of two or more dissolved solids contained within a solution in very small quantities. In Greek, the word ‘chroma’ means colour and ‘graphein’ is used to indicate writing. Initially, the technique was used for the separation of colors.
Substances that are separated during chromatography are called analytes. It is a physical process in which the solute (i.e. the components of a sample mixture) is separated due to the differential distribution between the stationary and mobile phases.
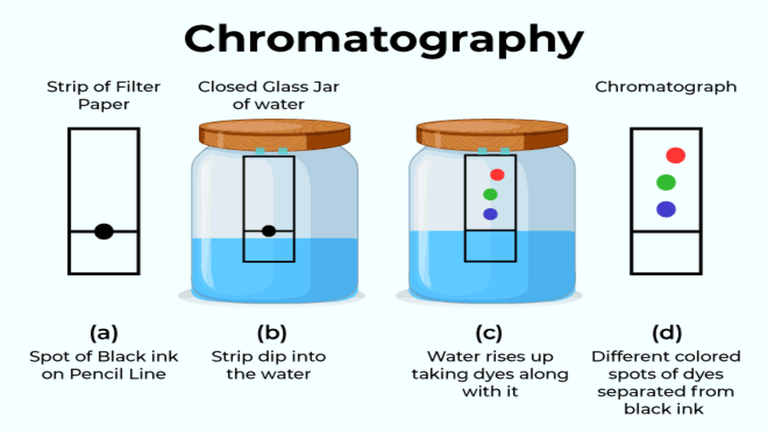
Terms used in chromatography
Let's learn some terms commonly used in chromatography
- Analyte: Analyte is a substance that is separated from a mixture during chromatography.
- Mobile Phase: In chromatography, the mobile phase is the substance that moves with the sample. It can be either gas or liquid, and the mixture is adsorbed as it passes through the column where the components of the mixture are adsorbed.
- Stationary Phase: In chromatography, stationary phase is a phase that does not move with the sample. It is a porous material that generally absorbs the material of the mobile period.
- Eluent: Eluent is the liquid that enters and passes through the chromatography column.
- Elute: Elute is the fluid containing the sample that exits the chromatography column.
- Elution: Elution is the process of removing or eliminating solids by rinsing them with a suitable solvent in column chromatography.

Principle of Chromatographic Technique
Chromatography is based on the principle where components in the mixture which are applied onto the surface or onto the solid or fluid stationary phase is separating from each other while moving with the aid of a mobile phase.
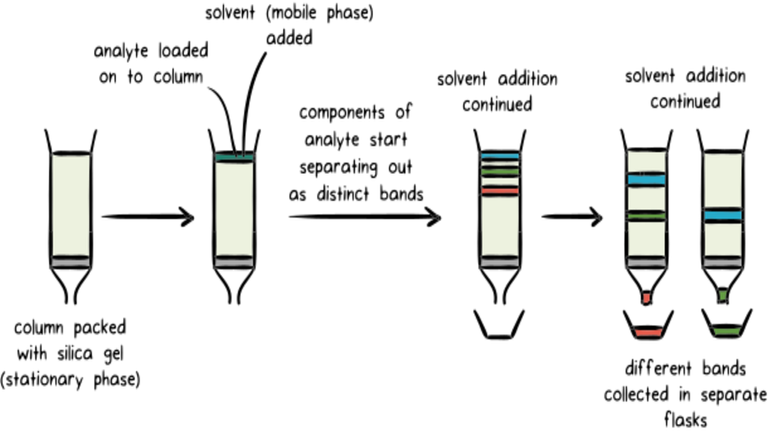
The factors effective only separation process include molecular characteristics related to absorption, partition and affinity or differences among their molecular weight. Because of these differences some component of the mixture stay longer in the stationary phase and they move slowly in the chromatography system while others passed rapidly into the mobile phase and leave the system faster.
The type of interaction between the stationary phase, mobile phase and substances contained in the mixture is the basic component effective on the separation of molecules from each other.

Types of Chromatography
Chromatography is a diverse and versatile analytical technique with numerous methods, each tailored to specific separation and analysis needs. Chromatography can be divided into several categories based on different methods and techniques. The main classifications of chromatography are:
According to the physical state of mobile and stationary phase:
- Gas Chromatography (GC): In GC, the mobile phase is a gas, usually an inert carrier gas such as helium or nitrogen, and the stationary phase is a liquid adsorbed onto a solid support. GC is often used to analyze volatile compounds.
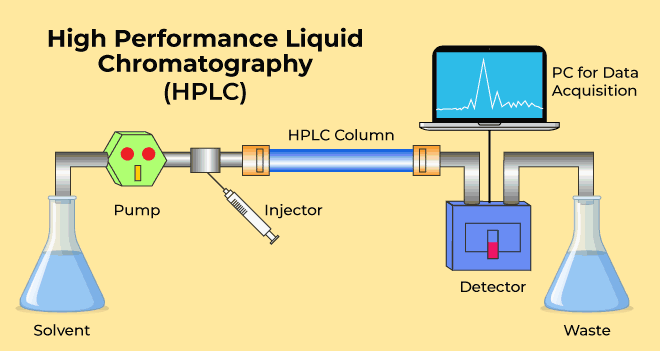
- Liquid Chromatography (LC): In LC, both mobile and stationary phases are liquid. LC methods include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), thin layer chromatography (TLC), and many more. LC is versatile and can be used for many class of compounds from polar to non-polar.
According to separation mechanism:
- Adsorption Chromatography: In this type of chromatography, the stationary phase is an adsorbent material (e.g., silica gel, alumina) that retains the analyte due to its interaction with the adsorbent surface.
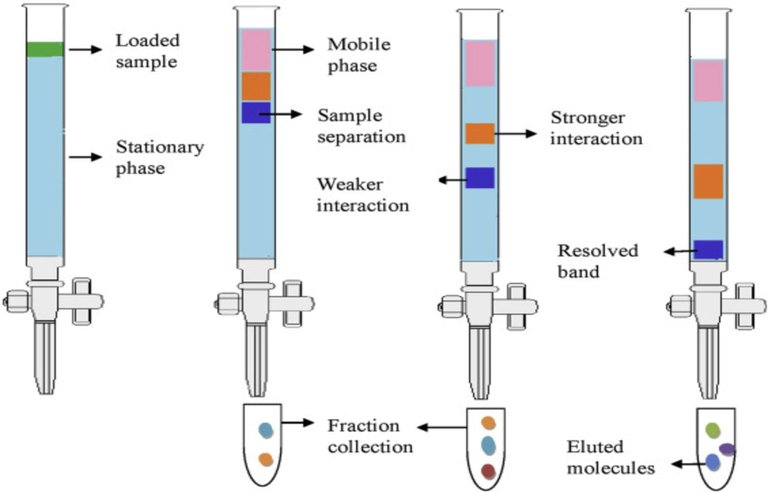
Partition chromatography: This method separates analytes based on their partitioning between two immiscible phases (stationary and mobile phases). Examples include normal phase chromatography and reverse phase chromatography.
Ion exchange chromatography: Ion exchange chromatography is based on reversible exchange of ions between analytes and charged sites on a stationary phase. It is used to separate ions and charged molecules.
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): SEC separates analytes based on their size and shape. Larger molecules elute first because they are excluded from the pores of the stationary phase.
Apart from these, as I mentioned already as chromatography is diverse and versatile, there are many more other types of chromatography such that based on the mode of application and purpose , based on the kind of detection method used or even could be based on the geometry of the column.

Chromatography in Our Lives
See, we mostly think this chromatography thing restricts its uses to some fancy chemicals in laboratory only, but that's not exactly the case. Well the diverse applications of chromatography do touch our lives and helps us out in various ways. This article will be incomplete if I don't bring light to those.
A Helping Hand in Medicine
Chromatography is an unsung hero in the world of medicine. Think about it: before a medicine reaches your pharmacy shelf, it goes through rigorous testing. Chromatographic techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) are like the detectives of the pharmaceutical world. They analyze drug compounds, making sure they are pure and potent. These techniques are also used to study how drugs move through our bodies, which is crucial for creating effective medications.

Keeping Our Food Healthy and Delicious
Have you ever wondered how to keep the food on your plate safe and delicious? Chromatography plays an important role in achieving this goal too. Whether it's vegetables in a salad or spices in your favorite meal, chromatography helps detect and identify pesticides, mycotoxins and pathogens. It ensures that the products we consume comply with the highest standards. What's more, it help experts understand the chemistry behind the flavors and aromas that make our food so delicious.
Protect Our Environment
Our environment faces challenges from pollution and contaminants. Chromatography comes as the guardian of our environment. It helps identify and quantify contaminants in air, water and soil. For example, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) monitors volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and persistent organic pollutants (POPs) to ensure we can take the necessary steps to protect our planet.
Unmasking Crime Mysteries
Chromatography even plays a starring role in solving crimes. It's like the Sherlock Holmes of the scientific world, helping forensic scientists analyze evidence from crime scenes. Gas chromatography identifies volatile substances like drugs and explosives, while liquid chromatography helps detect drugs in bodily fluids. These techniques have been pivotal in cracking numerous criminal cases, bringing justice to those who deserve it.

Conclusive thoughts
In the grand scheme of things, chromatography is much more than just a laboratory technique. It's an unsung hero that quietly but powerfully influences our daily lives. From making our food safer and medicines more effective to safeguarding our environment and aiding in solving crimes, chromatography's impact is undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, it will continue to open new doors in science and industry, ensuring that our world remains safer, healthier, and more informed. The colors of chromatography continue to paint a brighter and more vibrant future.
Until we meet again :)

Separation techniques: Chromatography, Ozlem Coskun
Principle of chromatography | Stationary phase
Colorful Clues: The Magical World of Chemical Indicators |ChemFam #63|
Colloids in Action: Impacting Your Daily Life More Than You Think |ChemFam #62|
The Complex Landscape of Opioid Analgesics: Addressing The Concerns |ChemFam #61|
Genetic Engineering: Pioneering Progress or Ethical Predicament? |ChemFam #60|
The Guardians Against Microbial Menace: Antibacterial Agents |ChemFam #59|
The Cholesterol Conundrum: The Story of Statins |ChemFam #58|
Unveiling The Control Of Chemistry: How Hormones Dictate Our Mood |ChemFam #57|
Thermodynamic Versus Kinetic Control of Reactions |ChemFam #56|
Bosons: The Quantum Glue That Holds The Universe Together |ChemFam #55|
Extraction of Lithium Using Electrode Materials of Lithium Ion Battery-II |ChemFam #54|
Extraction of Lithium Using Electrode Materials of Lithium Ion Battery |ChemFam #53|
Helium: The First Noble Gas |ChemFam #52|
Hydrogen: The Simplest Atom |ChemFam #51|
Elements, Atoms and Atomic Theory |ChemFam #50|
Have You Thanked A Clod Today? |ChemFam #49|
Nuclear Energy: Will It Rise Again? |ChemFam #48|
Soaps: An Essential and Effective Cleansing Agent |ChemFam #47|
Chemicals in Food : Debunking Myths and Ensuring Safe Consumptions |ChemFam #46|
Unveiling The Secrets of Antiseptics and Disinfectants |ChemFam #45|
What are Antimicrobials and Antimicrobial Drugs? |ChemFam #44|
Therapeutic Action of Different Classes of Drugs |ChemFam #43|
PS The thumbnail image is being created by me using canva.com



Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
Thank you @stemsocial
This post has been manually curated by @bhattg from Indiaunited community. Join us on our Discord Server.
Do you know that you can earn a passive income by delegating to @indiaunited. We share more than 100 % of the curation rewards with the delegators in the form of IUC tokens. HP delegators and IUC token holders also get upto 20% additional vote weight.
Here are some handy links for delegations: 100HP, 250HP, 500HP, 1000HP.
100% of the rewards from this comment goes to the curator for their manual curation efforts. Please encourage the curator @bhattg by upvoting this comment and support the community by voting the posts made by @indiaunited.
Thank you @bhattg and @indiaunited