17-02-2024 - Physics - Incident energy [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
17-02-2024 - Physics - Incident energy [EN]-[IT]
Basic concepts
Thermodynamics is a very broad science and I believe it is good to review certain basic concepts to be able to understand more complex things.
Below are some basic concepts.
What is Clapeyron's plan?
The Clapeyron plane is a Cartesian plane with orthogonal axes in which the volume value appears on the abscissa and the pressure value on the ordinate.
The different thermodynamic transformations can be represented on this plane; below I list some of them with their characteristics.
-Adiabatic transformation, on the Clapeyron plane it is a fairly inclined hyperbola
-Isothermal transformation, on the Clapeyron plane it is a rather not very inclined hyperbola
-Isobaric transformation, on the Clapeyron plane it is a straight line parallel to the abscissae.
-Isochoric transformation, on the Clapeyron plane it is a straight line parallel to the ordinates.
Incident Energy
To explain how the energy incident on the surface of a body is broken down, let us remember the concept of radiation.
Radiation is that phenomenon characterized by the emission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. By simply being at a certain temperature, all bodies emit radiant energy.
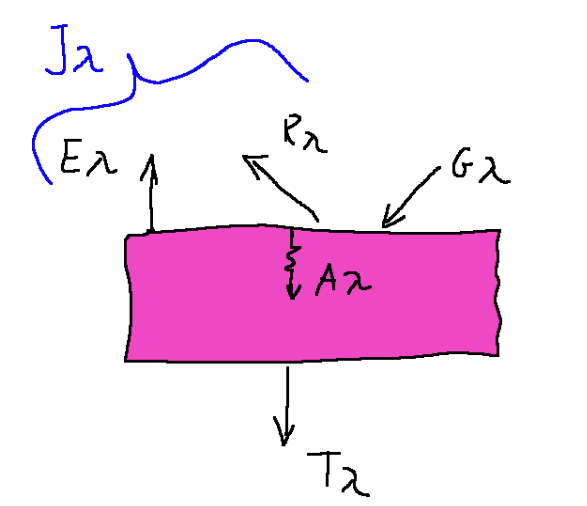
When a radiant energy G λ impacts the surface of a body, part of the radiation is reflected R λ while the remainder enters the body. This part, however, can be absorbed while the body is passed through, A λ.
If the material is transparent, part of the incident radiation will in turn be transmitted.
Below I list the factors that are at play to understand how the energy incident on the surface of a body is broken down.
G λ = Radiant energy
R λ = Reflected radiation
A λ = Energy absorbed
T λ =Incident radiation
The quantities G, R, A, T, that is, radiant energy, reflected radiation, absorbed energy, incident radiation, depend only on the wavelength.
Between these quantities there is a relationship that expresses an energy balance and is the following.
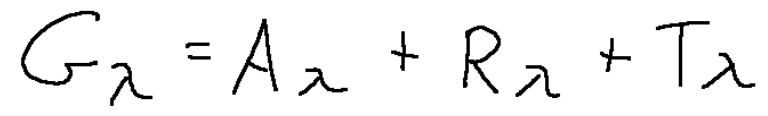
dividing all terms by G λ we will obtain the following relationship
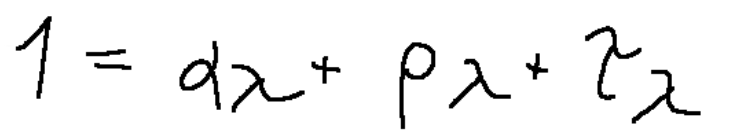
Where:
α λ = absorption coefficient
ρ λ = reflection coefficient
τ λ = transmission coefficient
We now introduce the term radiosity (J λ) which is the radiant energy that leaves a surface per unit of time and area.
This quantity includes the contributions of the incident and reflected energy, therefore it is to be considered different from the emissive power E λ
The graph below tries to show what has just been said.
Conclusions
When a radiant energy affects a surface of a body the following occurs. Part of the radiation is reflected, while the remaining part enters the body. This radiation can be absorbed as it passes through the body.
Request
Emissive energy and incident energy are terms that are usually mentioned when making a window. Have you ever heard these terms when choosing or viewing a home frame?

17-02-2024 - Fisica - Energia incidente [EN]-[IT]
Concetti base
La termodinamica è una scienza molto ampia e credo che sia bene ripassare certi concetti base per riuscire a comprendere le cose più complesse.
Qui di seguito alcuni concetti base.
Cosa è il piano di Clapeyron?
Il piano di Clapeyron è un piano cartesiano ad assi ortogonali nei quali compare in ascissa il valore del volume e in ordinata il valore della pressione.
Sul questo piano possono essere rappresentate le diverse trasformazioni termodinamiche, qui di seguito ne elenco alcune con le proprie caratteristiche.
-Trasformazione adiabatica, sul piano di Clapeyron è una iperbole abbastanza inclinata
-Trasformazione isoterma, sul piano di Clapeyron è una iperbole abbastanza non molto inclinata
-Trasformazione isobara, sul piano di Clapeyron è una retta parallela alle ascisse.
-Trasformazione isocora, sul piano di Clapeyron è una retta parallela alle ordinate.
Energia incidente
Per spiegare come si scompone l’energia incidente sulla superficie di un corpo ricordiamo il concetto dell' irraggiamento.
L’irraggiamento è quel fenomeno caratterizzato dall’emissione di energia sotto forma di onde elettromagnetiche. Per il semplice fatto di trovarsi ad una determinata temperatura, tutti i corpi emettono energia raggiante.
Quando un energia raggiante G λ incide sulla superficie di un corpo, parte della radiazione è riflessa R λ mentre la restante entra nel corpo. Questa parte però può essere assorbita mentre il corpo viene attraversato, A λ.
Se il materiale è trasparente una parte della radiazione incidente sarà trasmessa a sua volta.
Qui di seguito elenco i fattori che sono in gioco per capire come si scompone l’energia incidente sulla superficie di un corpo.
G λ = Energia raggiante
R λ = Radiazione riflessa
A λ = Energia assorbita
T λ =Radiazione incidente
Le grandezze G, R, A, T, ovvero, energia raggiante, radiazione riflessa, energia assorbita, radiazione incidente, dipendono solo dalla lunghezza d’onda.
Tra queste grandezze esiste una relazione che esprime un bilancio di energia ed è la seguente.
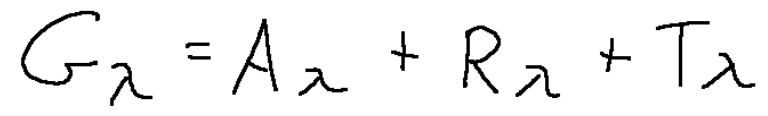
dividendo tutti i termini per G λ otterremo la seguente relazione
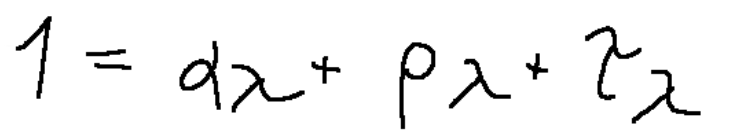
Dove:
α λ = coefficiente di assorbimento
ρ λ = coefficiente di riflessione
τ λ = coefficiente di trasmissione
Introduciamo ora il termine radiosità (J λ) che è l’energia raggiante che lascia una superficie per unità di tempo e di area.
Questa grandezza include i contributi dell’energia incidente e riflessa, perciò è da considerarsi diversa dal potere emissivo E λ
Il grafico qui sotto riportato prova a mostrare quanto appena detto.

Conclusioni
Quando un energia raggiante incide su una superficie di un corpo avviene quanto segue. Parte della radiazione è riflessa, mentre la restante parte entra nel corpo. Questa radiazione può essere assorbita mentre attraversa il corpo.
Domanda
Energia emissiva ed energia incidente sono termini che di solito vengono citati durante la realizzazione di una finestra. Vi è capitato di sentire questi termini durante la scelta o la visione di un infisso per abitazione?
THE END
This is an interesting lesson about the emission of radiant energy by bodies, and I enjoyed it. I want to ask if this is somehow connected with topology in mathematics? Thanks in advance for the answer. Have a great weekend.
Thanks for stopping by! There are two basic concepts in this article, perhaps the most important of the two is the one that explains what happens when a radiant energy affects a surface of a body.
When a radiant energy affects a surface of a body it happens that:
-part of the radiation is reflected
-the remaining part enters the body
Physics has tremendous is wide and is always enough to keep learning day by day
Thanks for stopping by. Emitted energy and incident energy are two interesting studies regarding heat transmission, in my opinion.
@tipu curate 2
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 34/54) Liquid rewards.
Grazie Roby per il tipu. Qui le cose potrebbero essere anche semplici. Per quanto riguarda l'energia incidente abbiamo 4 grandezze e la relazione che esiste è la seguente. L'energia incidente è uguale alla somma dell'energia assorbita + l'energia riflessa + l'energia trasmessa. Che tradotto con una formula si scrive così:
Gλ = Aλ + Rλ + Tλ
Thank you for this fantastic class
It was helpful
Hi @rafzat
When we talk about incident energy we have 4 quantities to manage which I report below.
Gλ = incident energy
Rλ = reflected energy
Aλ = energy absorbed
Tλ = energy transmitted
The relationship that exists between these is the following:
Gλ = Aλ + Rλ + Tλ
This means that the incident energy is equal to the sum of the absorbed energy + the reflected energy + the transmitted energy
!discovery 25
Grazie per il supporto Liberty. Visto che avevo scritto qualcosa sull'energia emessa, ho fatto un breve articolo anche sull'energia incidente.. giusto per non far calare la noia..hahaha
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
Grazie per il supporto
No, non ho mai sentito questo argomento prima.
Ciao LU, grazie per essere sempre presente: Ci sono due concetti base in questo articolo, forse quello più importante dei due è quello che spiega cosa avviene quando una energia raggiante incide su una superficie di un corpo.
Quando succede questo avviene che, parte della radiazione è riflessa, mentre la restante parte entra nel corpo. questa aliquota può essere assorbita mentre attraversa il corpo
This is really a well detailed class that is well explained. Thank you so much for taking your time to explain to us in details
Thanks to leave a comment.
When we talk about incident energy we have 4 factors to consider and they are the following: Gλ = incident energy
Rλ = reflected energy
Aλ = energy absorbed
Tλ = energy transmitted
I think this is important to keep in mind when we are talking about Incident energy