27-03-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (3/13)[EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
27-03-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (3/13)[EN]-[IT]
Mayer's report
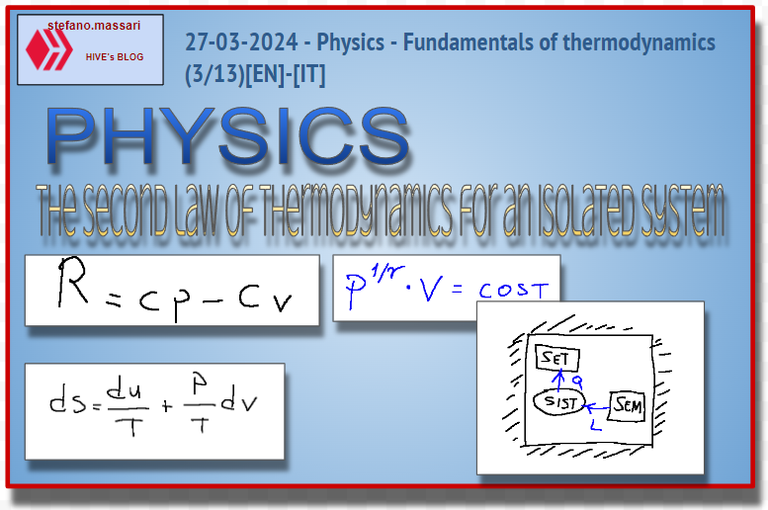
Mayer's relation states that the difference between Cp and Cv is always equal to the ideal gas constant.
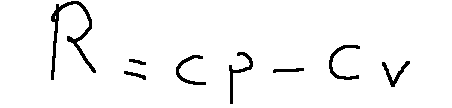
Where:
R = ideal gas constant
Cp = Molar specific heat at constant pressure
Cv = Molar specific heat at constant volume
Mayer's relation establishes that for a transformation at constant volume the molar specific heat Cv is generally lower than that at constant pressure Cp.
What comes from Mayer's report?
From Mayer's report we learn that at constant pressure it is necessary to supply more heat to vary the temperature of a mole of gas by 1°K, because part of the heat supplied is used by the gas to do work by varying its volume.
1st Gibbs equation
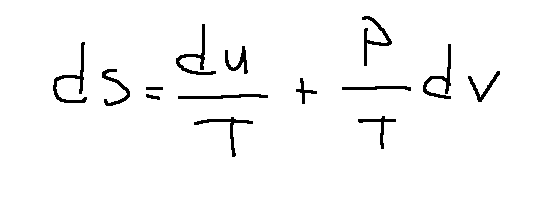
Notes on Isentropic Transformations
First of all, let's clarify the concept of isentropic transformation.
An isentropic transformation, in thermodynamics, is a transformation that occurs at constant entropy.
The ratio between the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume of a gas is of particular importance in calculations regarding the expansion and compression of gases.
The ratio between the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume of a gas is always greater than 1
An isentropic transformation is represented by the following equation:
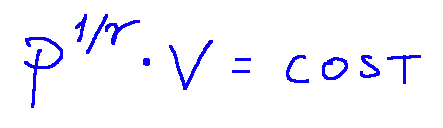
Clapeyron's plan
The Clapeyron plane is a Cartesian plane with orthogonal axes in which the volume value appears on the abscissa and the pressure value on the ordinate. It is used to study thermodynamic transformations.
NOTE:
Adiabatic transformation
(transformation that occurs without heat exchanges with the outside)
On the Clapeyron plane it is represented by an inclined hyperbola.
Isothermal transformation
(thermodynamic transformation at constant temperature)
On the Clapeyron plane a hyperbola is represented by a hyperbola less inclined than that of an adiabatic one.
Isobaric transformation
(thermodynamic transformation at constant pressure)
On the Clapeyron plane it is represented by a straight line parallel to the abscissae.
Isochoric transformation
(thermodynamic transformation in which the volume remains constant)
On the Clapeyron plane it is represented by a straight line parallel to the ordinates.
The T-S thermodynamic plane
In addition to the P-V plane (pressure - volume), thermodynamic transformations can be represented on the T-S plane (temperature - entropy)
In the T-S plane an isothermal transformation (at constant temperature) is represented as a straight line parallel to the abscissas.
In the T-S plane an adiabatic transformation (without heat exchange) is represented as a straight line perpendicular to the abscissas.
In the T-S plane the isochoric curve has a higher tangent than the isobaric one.
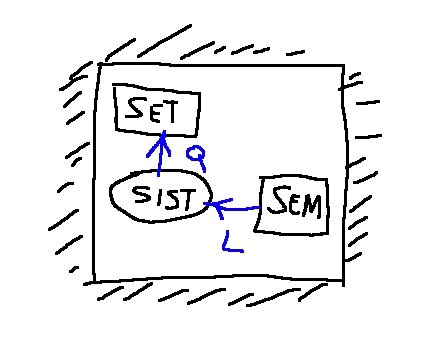
Thermodynamics of closed systems
Typical design of a closed thermodynamic system.
thermal tanks
Thermal or mechanical tanks are large systems that enjoy the property that the intensive variable associated with the flows always remains constant.
SET
The acronym SET refers to a thermal tank that only allows heat exchanges, following which its temperature does not vary.
Second law
The second law of thermodynamics for an isolated system states that it is not possible to create a heat machine capable of transforming all the heat into work.
Conclusions
The laws that concern thermodynamics are many and specific, in conclusion we can remember one of the most important laws of thermodynamics, that is, the second law of thermodynamics for an isolated system. This states that it is not possible to create a heat machine capable of transforming all the heat into work.
Request
Have you studied thermodynamic transformations on the P-V plane or on the T-S plane?

27-03-2024 - Fisica - Fondamenti di termodinamica (3/13)[EN]-[IT]
Relazione di Mayer
La relazione di Mayer afferma che la differenza tra Cp e Cv sempre uguale alla costante dei gas perfetti.
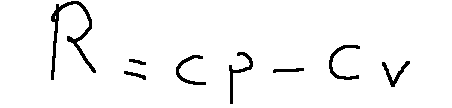
Dove:
R = costante dei gas perfetti
Cp = Calore specifico molare a pressione costante
Cv = Calore specifico molare a volume costante
La relazione di Mayer stabilisce che per una trasformazione a volume costante il calore specifico molare Cv è in generale minore di quello a pressione costante Cp.
Cosa scaturisce dalla relazione di Mayer?
Dalla relazione di Mayer si apprende che a pressione costante è necessario fornire più calore per far variare di 1°K la temperatura di una mole di gas, perché parte del calore fornito viene usato dal gas per compiere lavoro facendo variare il proprio volume.
1a equazione di Gibbs
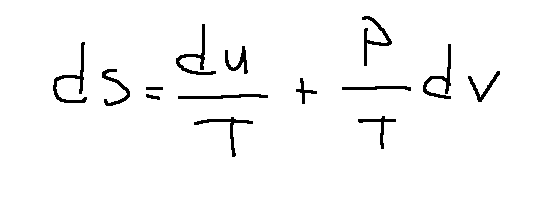
Note sulle Le trasformazioni isoentropiche
Prima di tutto chiariamo il concetto di trasformazione isoentropica.
Una trasformazione isoentropica, in termodinamica, è una trasformazione che avviene a entropia costante.
Il rapporto tra i calori specifici a pressione e a volume costante di un gas è di particolare importanza nei calcoli riguardante l'espansione e la compressione dei gas.
Il rapporto tra i calori specifici a pressione e a volume costante di un gas è sempre maggiore di 1

Una trasformazione isoentropica è rappresentata dalla seguente equazione:
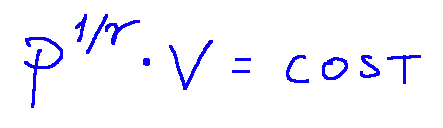
Il piano di Clapeyron
Il piano di Clapeyron è un piano cartesiano ad assi ortogonali nei quali compare in ascissa il valore del volume e in ordinata quello della pressione. Viene usato per studiare le trasformazioni termodinamiche.
NOTE:
Trasformazione adiabatica
(trasformazione che avviene senza scambi di calore con l'esterno)
Sul piano di Clapeyron è rappresentata da un iperbole inclinata.
Trasformazione isoterma
(trasformazione termodinamica a temperatura costante)
Sul piano di Clapeyron è rappresentata da un iperbole iperbole meno inclinata di quella che potrebbe essere quella di un adiabatica.
Trasformazione isobara
(trasformazione termodinamica a pressione costante)
Sul piano di Clapeyron è rappresentata da una retta parallela alle ascisse.
Trasformazione isocora
(trasformazione termodinamica in cui il volume rimane costante)
Sul piano di Clapeyron è rappresentata da una retta parallela alle ordinate.
Il piano termodinamico T-S
Oltre al piano P-V (pressione - volume), le trasformazioni termodinamiche possono essere rappresentate sul piano T-S (temperatura - entropia)
Nel piano T-S una trasformazione isoterma (a temperatura costante) è rappresentata come una retta parallela alle ascisse.
Nel piano T-S una trasformazione adiabatica (senza scambi di calore) è rappresentata come una retta perpendicolare alle ascisse.
Nel piano T-S la curva isocora ha tangente più elevata rispetto a quella isobara.
Termodinamica dei sistemi chiusi
Tipico disegno di un sistema termodinamico chiuso.

serbatoi termici
I serbatoi termici o meccanici sono dei sistemi di grandi dimensioni che godono della proprietà che la variabile intensiva associata ai flussi rimane sempre costante.
SET
Con la sigla SET si intende un serbatoio termico che consente solo scambi di calore, inseguito ai quali la sua temperatura non varia.
Seconda legge
La seconda legge della termodinamica per un sistema isolato stabilisce che non è possibile realizzare una macchina termica capace di trasformare tutto il calore in lavoro.
Conclusioni
Le leggi che riguardano la termodinamica sono tante e specifiche, in conclusione possiamo ricordare una delle leggi più importanti della termodinamica, cioè la seconda legge della termodinamica per un sistema isolato. Questa afferma che non è possibile realizzare una macchina termica capace di trasformare tutto il calore in lavoro.
Domanda
Avete vai studiato trasformazioni termodinamiche sul piano P-V oppure sul piano T-S?
THE END
Quite well explanatory and easy to understand. Physics is really wide
Physics is a science that has so many topics. In this article I think the part dedicated to the Clapeyron piano is interesting. This is a Cartesian plane in which there are pressure and volume values. On this plane the 4 main thermodynamic transformations are represented which are: isochoric, adiabatic, isothermal and isobaric
1-The isochoric transformation is represented by a straight line parallel to the ordinates
2-The adiabatic transformation is represented by a rather inclined hyperbola
3-The isothermal transformation is represented by a less inclined hyperbola than that of the adiabatic transformation
4-The isobaric transformation is represented by a straight line parallel to the abscissas
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 37/57) Liquid rewards.
Grazie Mad per il tag Tipu
Grazie MAD per aver lasciato un commento.. in questo post spiego come le trasformazioni termodinamiche possano essere rappresentate su due piani. Quello meno conosciuto è il pianto T-S, temperatura - entropia. Ho appunto fatto un cenno anche a questa tipologia di rappresentazione dove una trasformazione isoterma è una retta parallela alle ascisse, una trasformazione adiabatica è una retta perpendicolare alle ascisse e dove un isocora ha una tangente più elevata della isobara.
Qui di seguito ho riprodotto un grafico riassuntivo
Physics can be very wide and tough
Nice course and thanks for the explanation
Physics has evolved more and more over the last 200 years. Today is a huge universe! In this article I talk about the Mayer relation which has a certain importance in the thermodynamic field, but not everyone has heard of it. Mayer says that between the two molar specific heats the majority relation always exists which says that the molar specific heat at constant pressure is always greater than that at constant volume Cp>Cv
Ho letto la conclusione e la domanda, ma voglio solo augurarvi una buona notte, domani è Giovedì Santo e poi Venerdì Santo, chiediamo a DIO di aiutarci e proteggerci sempre, facciamolo con molta fede e si accadrà
Un abbraccio amico mio
Grazie per l'augurio. Per ora posso dire che il Sognore mi ha dato una mano a vivere. Grazie per aver letto anche questo articolo. In sostanza le cose più basilari di questi concetti sono:
-Per i calcoli riguardanti l'espansione e la compressione di un gas è di particolare importanza il rapporto tra i calori specifici a pressione e a volume costante
-La seguente formula rappresenta una trasformazione isoentropica
-Il rapporto tra i calori specifici a pressione e a volume costante è sempre maggiore di 1, tanto è vero che vale la seguente relazione.
La formula del rapporto
!discovery 30
In questo articolo una delle cose principali di cui parlo è la relazione di Mayer.. non molti la citano quando si parla di termodinamica, eppure è piuttosto importante. La formula è la seguente:
La relazione di Mayer sostanzialmente stabilisce che per una trasformazione a volume costante il calore specifico molare Cv è in generale minore di quello a pressione costante Cp.
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program