Moto circolare uniforme - esercizio-01 [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
Uniform circular motion
Uniform circular motion is a motion studied in physics and is the motion of a body describing a circular trajectory.
The velocity of a body moving on a circular trajectory is called tangential velocity.
The tangential velocity represents the length of circumference traveled during the rotation period T.
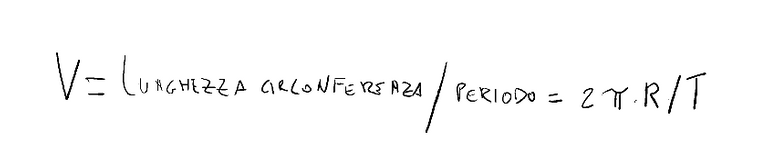
π = 3,14
R = the radius of the circumference
T = the period of rotation, that is, the time it takes to complete one full revolution.
Let us now introduce the concept of angular velocity.
This is the ratio of the angle swept to the time taken to sweep it.
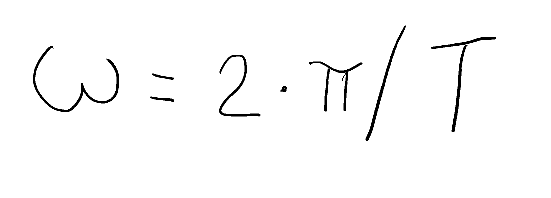
Another concept to introduce is that of the frequency of motion, which would be how many complete revolutions you have swept in 1 second and is equal to the inverse of the period.
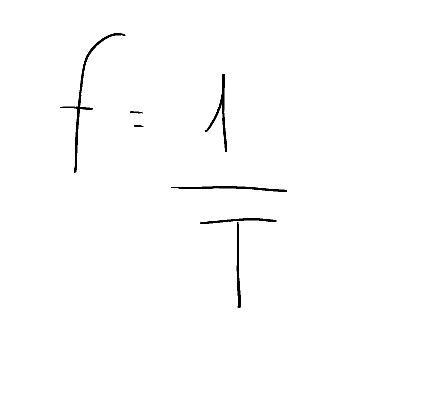
The last concept we introduce today is that of centripetal acceleration.
It affects the change in the direction of the velocity along the circular trajectory.

Exercise:
A point moves along a circumference of radius 25 m.
The tangential velocity is 15 m/s.
What is the period T of the motion?
Let's immediately think back to the first formula in which period T is present, I'll reproduce it below.
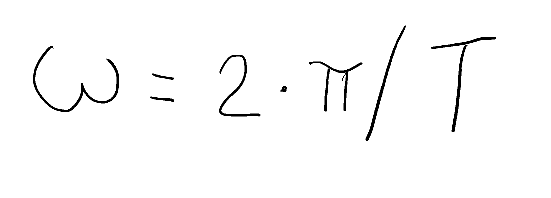
From this formula we can directly derive the period.
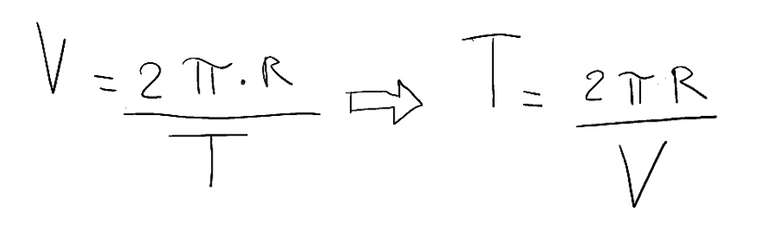
So we have that T the period of rotation, that is, the time it takes to make one complete revolution is....
T = 10.46 s

ITALIAN
Il moto circolare uniforme
Il moto circolare uniforme è un moto studiato dalla fisica ed è il moto di un corpo che descrive una traiettoria circolare.
La velocità di un corpo che si muove su una traiettoria circolare si chiama velocità tangenziale.
La velocità tangenziale rappresenta la lunghezza di circonferenza percorsa durante il periodo di rotazione T.
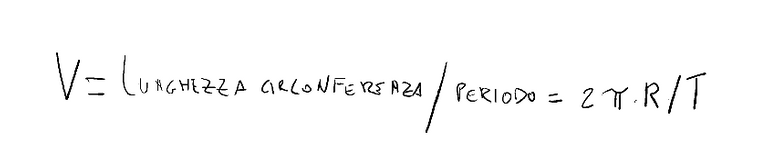
π = 3,14
R = il raggio della circonferenza
T = il periodo di rotazione, cioè il tempo necessario per compiere un giro completo.
Introduciamo ora il concetto di velocità angolare.
Questa è il rapporto tra l'angolo spazzato e il tempo impiegato a spazzarlo.
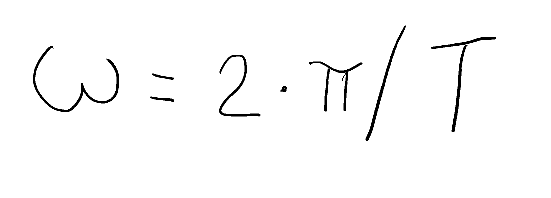
Altro concetto da introdurre è quello della frequenza del moto che sarebbe quanti giri completi si sono percorsi in 1 secondo ed è uguale all'inverso del periodo.
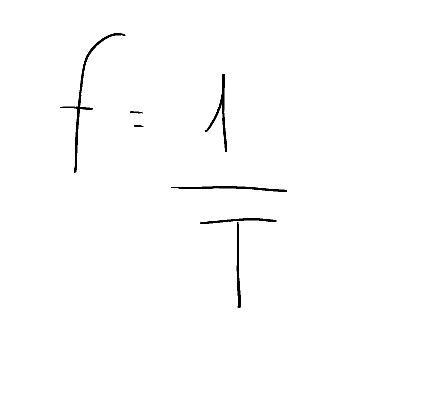
L'ultimo concetto che introduciamo oggi è quello dell'accelerazione centripeta.
Essa influisce sulla variazione della direzione della velocità lungo la traiettoria circolare.

Esercizio:
Un punto si muove lungo una circonferenza di raggio 25 m.
La velocità tangenziale è di 15 m/s
Qual è il periodo T del moto?
Ripensiamo subito alla pima formula in cui è presente il periodo T, la ripropongo qui sotto.
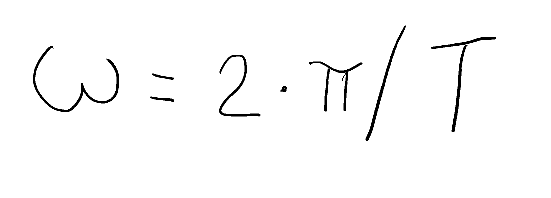
Da questa formula possiamo ricavare direttamente il periodo.

Quindi abbiamo che T il periodo di rotazione, cioè il tempo necessario per compiere un giro completo è....
T = 10,46 s
THE END
Wow back to school
Stavo proprio pensando che diffondere ció che abbiamo imparato è un bene per tutti, inoltre veniamo anche ricompensati
https://twitter.com/127503784/status/1650407671084855296
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.