DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS: THE SAME OR DIFFERENT
DIFFUSION
Diffusion is the random movement of molecules of gases, fluid and solid from a region where their concentration is high to a region where their concentration is lower until the concentration in all regions are the same(equilibrium).
Importance of Diffusion
1.) Exchange of gases between organisms and their environment e.g mesophylls of leaves.
2.) It enhances the movement of gases during photosynthesis.
3.) It promotes mineral salts uptake by roots.
4.) Removal of excretory products in unicellular organisms.
Characteristics of Diffusion
1.) The molecules or ions diffuse form regions of their higher concentration to region of their lower concentration.
2.) The diffusing molecules move randomly towards all the regions of their lower concentration.
3.) The movement of molecules is due to the kinetic energy.
4.) The direction of diffusion of one substance is independent of the movement of another substance.
5.) The rate of diffusion of molecules is proportional to their kinetic energy, their size, the density of medium through which they move and the gradient of concentration.

Factors Affecting Diffusion
1.) Size of particles or molecules: The larger molecules diffuse slower than small particles.
2.) Temperature: The rate of diffusion increases with increase in temperature.
3.) Solubility of solutes: Diffusion of solute molecules in a particular solvent depends upon their solubility in that solvent. Greater solubility leads to high rate of diffusion.
4.) Medium in which diffusion occurs: The rate of diffusion would be slower if the medium is concentrated that is, increase in the number of foreign molecules causes the rate of diffusion to decrease.
5.) Concentration gradient: This is the difference in the concentration of the diffusion molecules. The steeper the diffusion pressure gradient the faster s the rate of diffusion.
6.) State of matter: Gases diffuse faster than liquids and liquids faster than solids.
OSMOSIS
Osmosis is defined as the movement of solvent molecules or water molecules from a region of their high concentration to the region of their low concentration through a differentially permeable membrane.
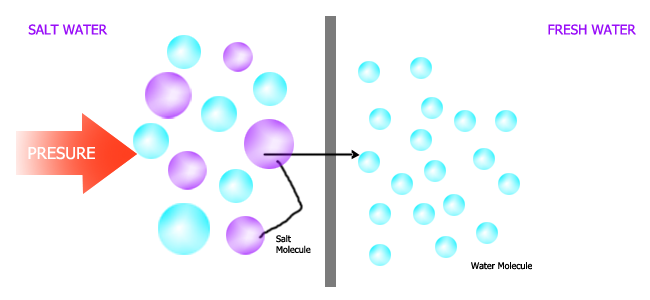
Significance of Osmosis
1.) It enhances the absorption of water from soil into the root of plants.
2.) It is the basis of movement of water from one living cell to another within the plant that is root, through stem to leaves.
3.) It helps plant cells retain water and keep their shape and turgidity.
4.) It controls the opening and closing of the stomata.
SIMILARITIES AND DIFFERENCES BETWEEN DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
There exist a load of comparism as well as differences between diffusion and osmosis. We will be looking at the similarities first then later proceed to the differences.
Similarities between diffusion and osmosis
1.) Particles move from region of high concentration to a region of low concentration in both osmosis and diffusion.
2.) They both regulate the concentration of the particles.
Differences between diffusion and osmosis
1.) In diffusion, both solute and solution moves to and fro but only solute moves in osmosis.
2.) Diffusion occurs in all phases be it solid , liquid or gas while osmosis occurs only in liquid phase.
3.) Diffusion does not occur a semipermeable membrane for it to occur while osmosis requires a semipermeable membrane.
4.) Diffusion does not depend on solute potential or solvent potential while osmosis depend on solute potential.
5.) Diffusion is a fast process while osmosis is a slow process.
References
Differences between osmosis and diffusion
Diffusion
Osmosis
Similarities between diffusion and osmosis
Muy buena la explicación, estos conceptos son muy importantes para comprender procesos biológicos. Saludos
Excellent explanation friend, it is worth sharing it an extremely important material in plant physiology.